Figure 2.
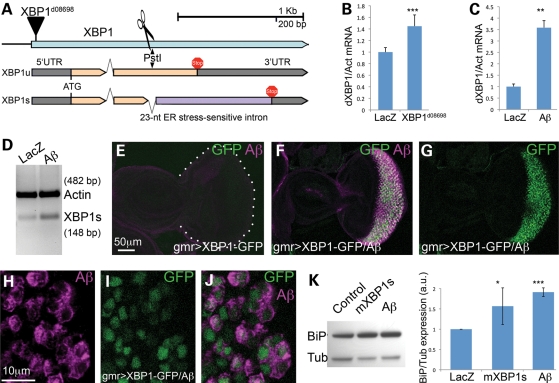
Unconventional splicing of XBP1. (A) Genomic map of the XBP1 locus in Drosophila. The XBP1d08698 insertion that regulates XBP1 expression is located in the 5′ UTR. XBP1 produces two isoforms that differ in the inclusion (XBP1u) or exclusion (XBP1s) of a 23-nucleotide intron subjected to cytoplasmic splicing. The site for PstI digestion inside the 23 bp intron is also shown. (B) The XBP1d08698 insertion induces XBP1 expression. Combination of da-Gal4 with XBP1d08698 induces a 40% increase in total XBP1 mRNA compared with flies expressing LacZ (control) by qPCR. (C) Aβ induces XBP1 expression. Flies expressing Aβ under the control of da-Gal4 induce a 3.5-fold increase in total XBP1 transcripts compared with LacZ control flies. In (C) and (D), XBP1 expression was normalized to Actin. (D) Aβ induces XBP1 unconventional splicing. Flies expressing Aβ under the control of da-Gal4 accumulate higher amounts of the XBP1s isoform than control flies expressing LacZ. Actin is shown as loading control. (E–J) Aβ activates XBP1 splicing in vivo. (E) Control flies expressing the XBP1–GFP sensor in the eye (gmr-Gal4/UAS–XBP1–GFP) do not produce GFP. (F and G) Flies co-expressing Aβ and the sensor (gmr-Gal4/UAS–Aβ/UAS–XBP1–GFP) accumulate Aβ (magenta, F) and high levels of GFP (green, F and G) in the same territory of the developing eye. (H–J) All the cells expressing Aβ also accumulate GFP, although the two signals do not co-localize because Aβ is in the membrane and GFP is nuclear. (K) Both mXBP1s and Aβ induce Grp78/BiP upregulation. Heads from flies expressing a control transgene (LacZ), mXBP1s or Aβ were homogenized, resolved in western blot and incubated with BiP and Tubulin antibodies. BiP appears significantly upregulated in flies expressing mXBP1s and Aβ (n= 3).