Figure 4.
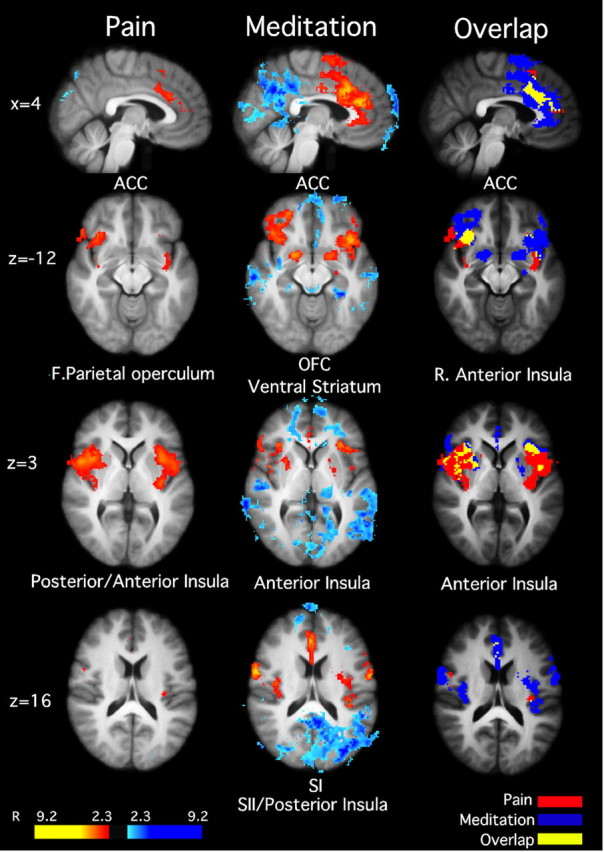
Brain activations and deactivations illustrate the main effects of pain and meditation, as well as the overlap between pain and meditation in MRI session 2 (after training). Noxious stimulation activated the ACC, bilateral anterior insula, and posterior insula/SII. Meditation activated bilateral ACC, OFC, ventral striatum, anterior insula, SI, and SII. Moreover, meditation was associated with deactivations in the medial PFC and posterior cingulate cortex, consistent with default mode network activation. There was significant overlap between meditation and pain in the ACC and anterior insula, suggesting that these areas serve as a possible substrate for pain modulation. Slice locations correspond to standard stereotaxic space.
