Figure 6.
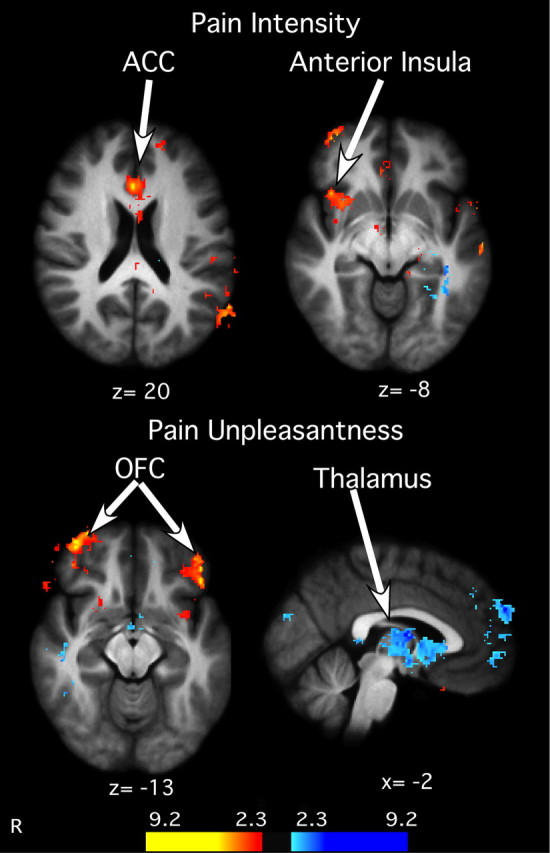
Relationship between meditation-induced decreases in psychophysical pain ratings and pain-related brain activation. Subjects reporting the greatest decrease in pain intensity ratings also exhibited the largest increase in the ACC and right anterior insula activation. Top, Similarly, subjects reporting the greatest activation in the OFC exhibited the greatest decreases in pain unpleasantness. In contrast, greater deactivation in the thalamus was related to larger decreases in pain unpleasantness ratings. Bottom, Slice locations correspond to standard stereotaxic space.
