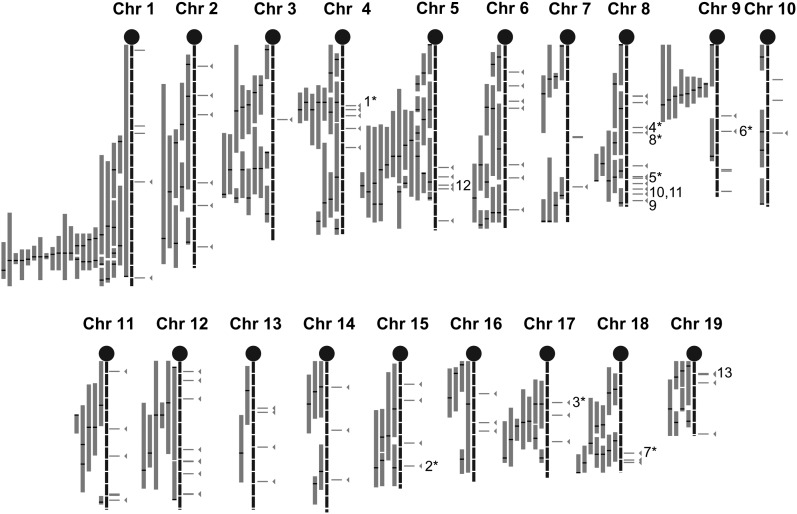
Fig. 1.
Mouse HDL QTL map overlapped with the homologous genes identified in a human GWA study. HDL QTL information was gathered from Wang and Paigen (2). We updated this list with recent HDL QTL results. A QTL is defined as a main effect QTL with a suggestive or significant LOD score as reported in the study. Each QTL peak positions, CIs, strains, sex, diet, and reference study are indicated in supplementary data (supplementary Tables I, II). Gray bars represent the 95% CI of each mouse QTL, black bars indicate QTL peaks. SNPs from the GWA study with a P < 10−3 were selected and binned by linkage disequilibrium using r2 = 0.5. Horizontal gray lines to the right of the chromosomes represent the 92 selected GWA study hits (bins), lines with arrows represent genes falling within the 95% CI of the HDL QTL. Genes discussed in this report are also indicated in this map: Abca1 (1), Ppara (2), Angptl4 (3), Cpe (4), Lcat (5), Lipc (6), Lipg (7), Lpl (8), Galnt2 (9), Cdh13 (10), Wwox (11), Mvk/Mmab (12), Fads1/Fads2 (13). Numbers with * indicate a gene with a reported in vivo mouse model (knock-out, transgenic or mutant mouse) showing a variation in HDL level compared with controls.