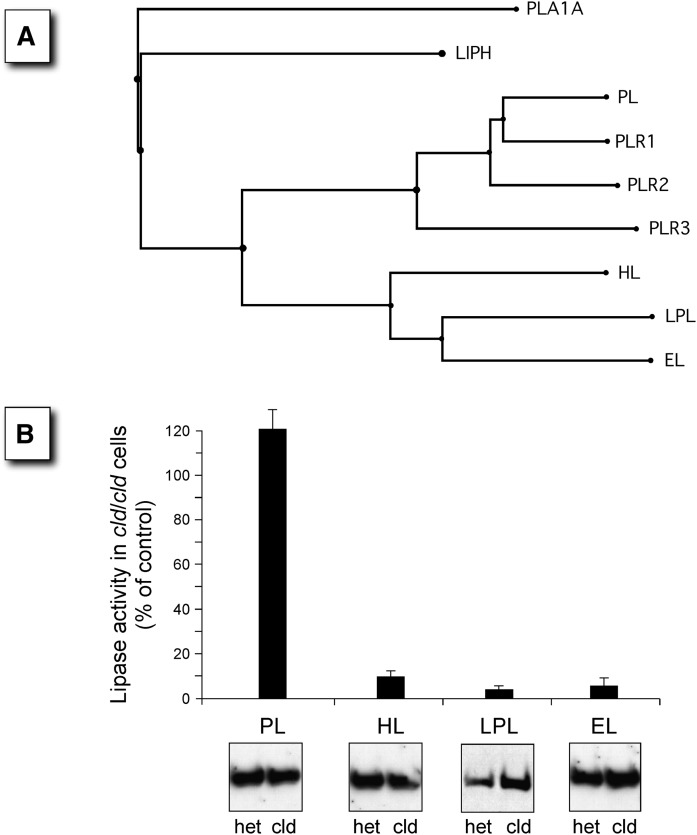
Fig. 1.
Members of the lipase gene superfamily that are affected by the cld mutation are shown. A: The phylogenetic tree of the lipase gene family shows a group of closely related members (HL, LPL, and EL) that form homodimers compared with the more distantly related PL, which is active as a monomer. The subunit structure of the remaining members is not known. All members of the family are secreted enzymes, and thus, all mature within the ER. The members include PLA1A, phospholipase A1 member A (Q53H76); LIPH, lipase member H (Q8WWY8); PL, pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase (P16233), and the three PL-related lipases, PLR1 (P54315), PLR2 (P54317), and PLR3 (Q17RR3); HL, hepatic triacylglycerol lipase (P11150); LPL, lipoprotein lipase (P06858); and EL, endothelial lipase (Q9Y5X9). B: The four members of the lipase gene family with known subunit structures were transfected into cells homozygous for the cld mutation (cld/cld), and expressed lipase activity was compared with that of control cells carrying only one copy of the cld allele (+/cld). Panels show representative Western blots of total cell lysates visualized using an antibody against a lipase-specific epitope tag.