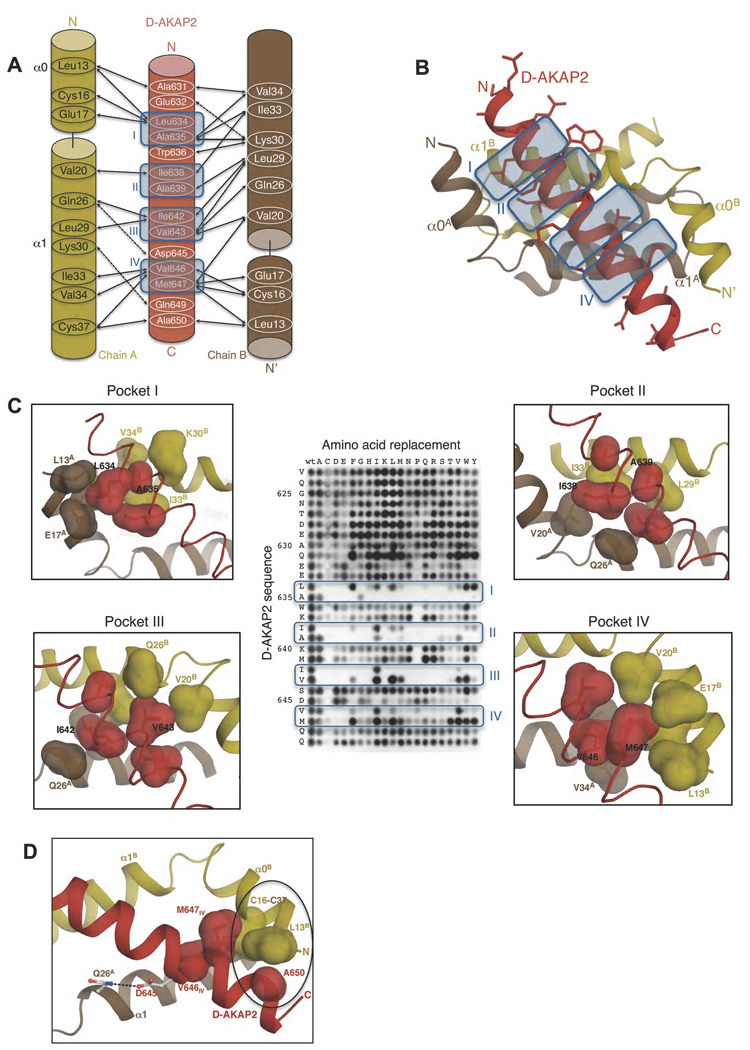
Figure 3. Interactions between RIα D/D and D-AKAP2.
(A) Schematic figure detailing the interactions between the side chains of D-AKAP2 and RIα D/D monomers. Solid and dashed arrows indicate hydrophobic and polar interactions respectively. Pockets I-IV are indicated by blue-colored boxes and numbered. (B) Overall structure showing the interaction. The structures are colored as panel (A). The side chains of D-AKAP2 are also shown to indicate the interface of binding. The pockets are indicated by blue-colored boxes and numbered. (C) Close-up views of pockets I through IV correlated with peptide array data. The coloring scheme is similar to Figure 3A. Previous peptide array data (Burns-Hamuro et al., 2003) are shown to highlight the stringent requirements for D-AKAP2 binding to RIα D/D (Copyright 2003, National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A). The surfaces of residues involved in each pocket are shown to highlight the tight packing interactions at the interface. (D) View of additional hydrophobic and polar interactions that stabilize RIα D/D:D-AKAP2 interaction. The coloring scheme is similar to Figure 3A. The residues involved in the hydrophobic interaction are represented as surfaces and circled. Hydrogen bonds between residues are indicated by dashed lines. For orientation, pocket IV residues, V646 and M647, are also shown.