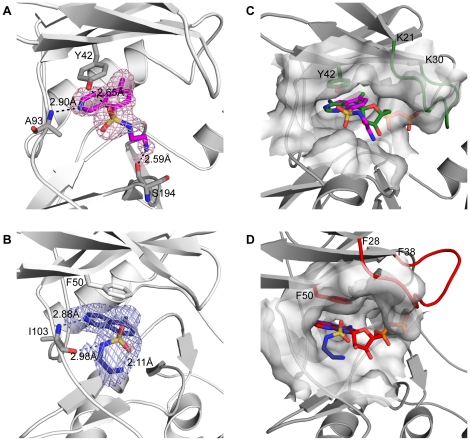
Figure 2. Nucleotide/inhibitor binding sites of APH(3′)-IIIa and APH(9)-Ia.
The CKI-7- and nucleotide-bound APH(3′)-IIIa are shown in cartoon representation in panels A and C respectively; The CKI-7- and nucleotide-bound APH(9)-Ia are shown in cartoon representation in panels B and D, respectively. (A) CKI-7 bound to APH(3′)-IIIa in magenta sticks and its simulated annealing Fo-Fc omit map, contoured at 2.5σ, are shown. Tyr42, which forms stacking interactions with the isoquinoline, and Ala93, which hydrogen bonds with the inhibitor, are shown in sticks. (B) CKI-7 bound to APH(9)-Ia in dark blue sticks and its simulated annealing Fo-Fc omit map, contoured at 2.5σ, are shown. Phe50 whose aromatic ring stacks with the isoquinoline, and Ile103, which forms hydrogen bond interactions with the inhibitor, are shown in sticks. (C,D) Comparison of the inhibitor- and nucleotide-bound APHs. The homologous ePK gly-rich loop is highlighted in green for nucleotide-bound APH(3′)-IIIa (C) and red for APH(9)-Ia (D). Tyr42 in APH(3′)-IIIa and Phe50 in APH(9)-Ia, that stacks the adenine ring of the nucleotide are shown in sticks and their carbon atoms are colored green for APH(3′)-IIIa (C) and red for APH(9)-Ia (D). The CKI-7-binding sites are delineated by surface representation in their respective enzymes. CKI-7 bound to APH(3′)-IIIa and APH(9)-Ia are colored as in panels A and B. CKI-7 binds to the same region and in an analogous manner as the nucleotide to each of the enzyme. The phosphates of the nucleotide are buried in the surface representing the homologous gly-rich loop in the presence of CKI-7.