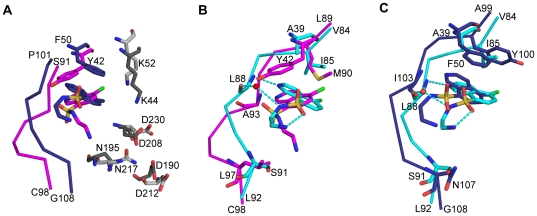
Figure 3. Comparisons of CKI-7 binding to APH(3′)-IIIa, APH(9)-Ia and CK1.
The structures are superposed using the conserved residues among the enzymes. (A) Superposition of CKI-7-bound APH(3′)-IIIa and APH(9)-Ia. The conserved active site residues between APH(3′)-IIIa and APH(9)-Ia are colored dark grey and light grey respectively. The APH(3′)-IIIa-bound CKI-7 is shown as magenta sticks and the APH(9)-Ia-bound CKI-7 is shown as dark blue sticks. The rotation between the planes of the isoquinoline rings of CKI-7 bound to APH(3′)-IIIa and APH(9)-Ia is approximately 40°. (B) Superposition of CKI-7-bound APH(3′)-IIIa and CK1. The same degree of rotation as that observed between the isoquinolines of the APH(3′)-IIIa- and APH(9)-Ia-bound CKI-7 is observed here. (C) Superposition of CKI-7-bound APH(9)-Ia and CK1. The CKI-7 isoquinoline rings are coplanar. In panels (B) and (C), APH(3′)-IIIa and APH(9)-Ia are colored as in panel A, and CK1 is colored in cyan. The residues that interact with CKI-7 and those with dissimilar properties from ePK nucleotide-binding site are shown in sticks. Hydrogen bond interactions between CKI-7 and CK1 are illustrated as dash lines. Water molecule is represented by a red sphere.