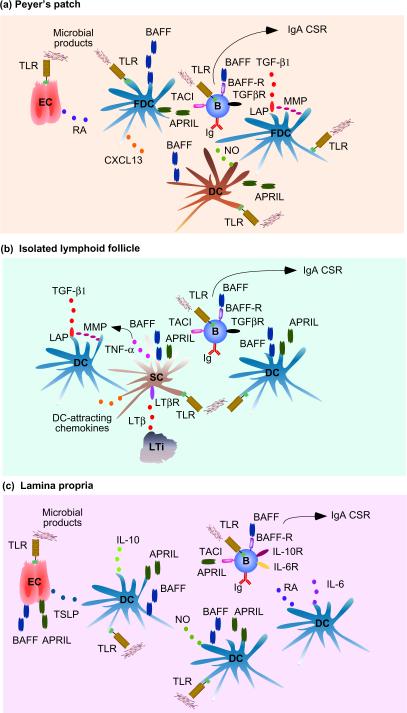
Figure 1.
BAFF and APRIL signaling networks in B cells. (a) TLR-activated epithelial cells (ECs) from Peyer's patches release retinoic acid (RA), which “primes” TLR-activated FDCs to produce BAFF, APRIL, the B cell-attracting chemokine CXCL13 as well as MMPs. These enzymes generate active TGF-β1 from latency-associated peptide (LAP). As well as producing additional BAFF and APRIL, TLR-activated TipDCs release nitric oxide (NO), which up-regulates TGF-β1 receptor (TGFβR) on B cells. In the presence of B cell-intrinsic TLR signals, engagement of TACI, BAFF-R and TGFβR by BAFF, APRIL and TGFβ stimulates IgA CSR and secretion. (b) Lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) cells from isolated lymphoid follicles release LTβ, which enhances production of TNF and DC-attracting chemokines in local TLR-activated stromal cells (SCs). TNF up-regulates the expression of MMPs and release of TGF-β1 in TLR-activated DCs, which also secrete BAFF and APRIL as TLR-activated SCs do. BAFF, APRIL and TGF-β stimulate follicular B cells as in (a). (c) TLR-activated ECs from the lamina propria release BAFF, APRIL and TSLP, which elicits BAFF, APRIL as well as IL-10 production, in TLR-activated myeloid DCs. NO from TLR-activated TipDCs further enhances DC production of BAFF and APRIL. Another DC subset releases RA and IL-6, which promote IgA secretion. BAFF, APRIL and TGF-β stimulate follicular B cells as in (a) together with engagement of IL-10R, IL-6R and retinoic acid receptor (not shown). APRIL, a proliferation-inducing ligand; BAFF, B cell-activating factor of the TNF family; CSR, class switch recombination; DC, dendritic cell; FDC, follicular dendritic cell; MMP, matrix metalloprotease; TACI, transmembrane activator and calcium-modulating ciclophilin-ligand interactor; TLR, Toll-like receptor.