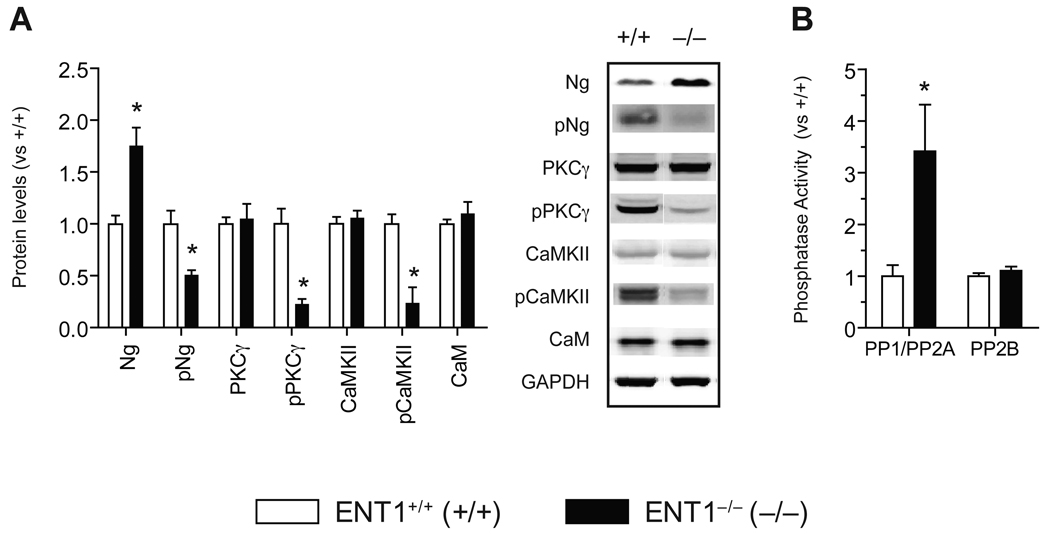
Figure 2.
Altered signaling molecules in the NAc of ENT1−/− mice. (A) Expression of signaling molecules in the NAc of ENT1−/− mice. Ng is increased [t(14) = 3.95, p = 0.0015] while pNg (Ser36) is reduced in ENT1−/− compared to ENT1+/+ mice [t(14) = 3.84, p = 0.002]. PKCγ is not altered while pPKCγ (Thr514) is significantly reduced in ENT1−/− mice compared to ENT1+/+ mice [t(20) = 4.99, p < 0.001]. CaMKII levels are similar while pCaMKII (Thr286) is significantly reduced in ENT1−/− mice compared to ENT1+/+ mice [t(14) = 2.51, p = 0.024]. CaM levels are similar between genotypes. Representative blots and expression levels are expressed as fold change compared to ENT1+/+ mice after normalization by GAPDH. n = 8 ~ 11 for each genotype; *p < 0.05 compared to ENT1+/+ mice after normalization by GAPDH (unpaired, two-tailed t-test). (B) Altered protein phosphatase activity in the ENT1−/− mice. PP1/PP2A activity is increased in the NAc of ENT1−/− mice [t(16) = 2.9, p = 0.02], whereas PP2B (calcineurin) activity is not changed in the NAc. n = 8~10 for each genotype; *p < 0.05 compared to ENT1+/+ mice by unpaired two-tailed t-test. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.