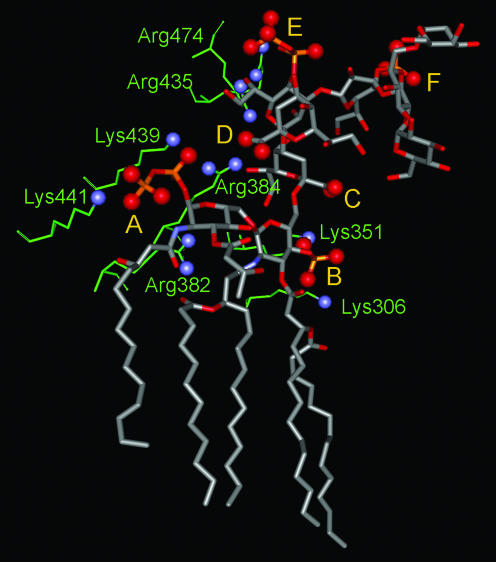
FIG. 12.
Electrostatic interactions between the E. coli LPS and the FhuA protein. The LPS structure is shown in a ball-and-stick diagram, with the oxygen atoms in the acidic moieties indicated by large red balls. A, B, C, D, E, and F refer to the 1-pyrophosphate of GlcNI (the reducing glucosamine), the 4′-phosphate of GlcNII (the nonreducing glucosamine), KDOI carboxylate, KDOII carboxylate, the HepI 4-pyrophosphate, and the HepII 4-phosphate, respectively. The amino acid residues apparently interacting with these anionic groups are shown as thin green sticks, with the basic nitrogen atoms indicated by blue balls. The amino acid residues making tight interactions are discussed in the text. The numbering of residues here is that of the engineered FhuA, which contains an 11-residue insertion after Pro405. Thus, Lys439 and Lys441 here correspond to Lys428 and Lys430 of the native FhuA, the numbering used in Table 1 of reference 203. In addition, the following residues make somewhat longer-range interactions: Arg382 with the secondary phosphate of 1-pyrophosphate (4.6 Å); Lys306 with 4′-phosphate (6 to 7 Å); Lys351 and Arg384 with KDOI carboxylate (4.7 and 7 Å); Lys439 with KDOII carboxylate (4.9 Å); and Arg474 and Arg435 with HepI 4-pyrophosphate (4.7 and about 10 Å). The figure was drawn with DS Viewer Pro (Accelrys, San Diego Calif.) using PDB file 1QFG. In addition to these electrostatic interactions, some amino acid residues may be involved in H-bonding interactions, which are not shown.