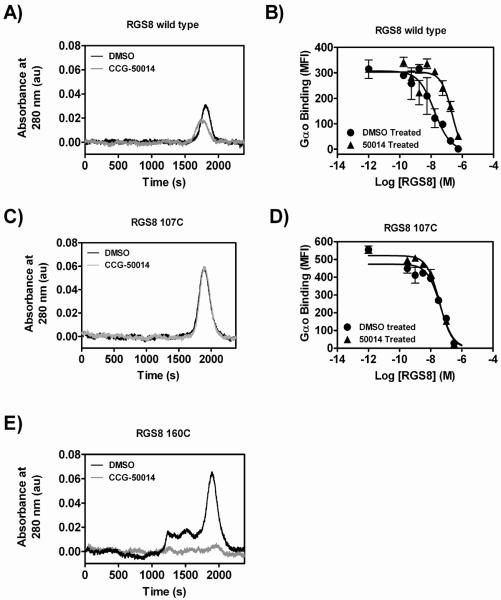
Figure 6. CCG-50014 induced protein aggregation is dependent on the presence of 160C.
A,B) Wild type, C,D) 107C, or E) 160C RGS8 was treated with a 5-fold excess of CCG-50014 before removal of the compound via gel filtration on a 20 mL S75 superdex column. A,C,E) Shown are representative UV chromatogram traces. B,D) Protein recovered from the peak was tested for Gαo binding in an FCPIA competition assay with AF532-Gao binding to WT RGS8. The wild-type RGS8 chromatogram shows a slightly left shifted and suppressed peak after CCG-50014 treatment, which coincides with a 14-fold decrease in Gαo binding. The 107C mutant protein showed no CCG-50014-induced change in migration on gel filtration and any inhibition of Gαo binding activity was reversed by the gel filtration procedure. The 160C mutant protein completely (and visually) aggregates upon compound treatment and is removed by the prefiltration of the samples.