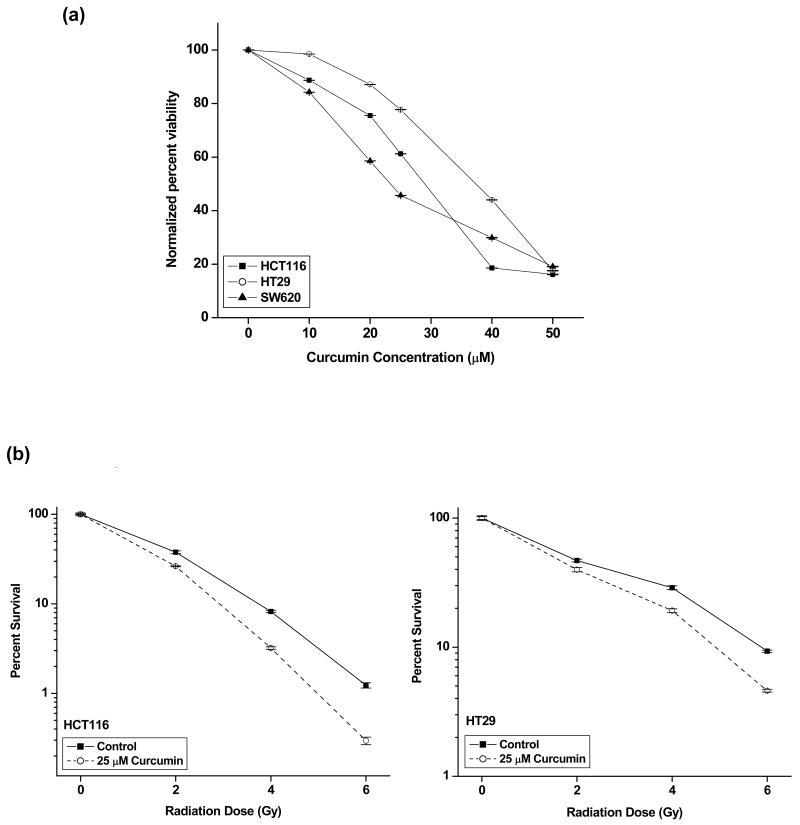
Figure 1. Curcumin augments radiation-induced cytotoxicity in colon cancer cells.
(a) Cells (3 × 104/mL) were exposed to different doses of curcumin in 96-well plate for 4 h after which the curcumin was washed and fresh medium was added to cells. Viability was assessed by XTT assay (Roche) after 48 h. The percent viability was calculated with respect to DMSO-treated controls. Points, mean of quadruplicates for each concentration; bars, SE. (b) HCT116 and HT29 cells were exposed to 25 μM curcumin for 4 h, and irradiated at indicated doses. Cells were re-plated for clonogenic assay 3 h post-radiation. The enhancement in radiosensitivity by curcumin was assessed on the basis of percent cell survival in comparison with the controls (cells irradiated with DMSO). Points, mean of the sextuplicates, bars, SE.