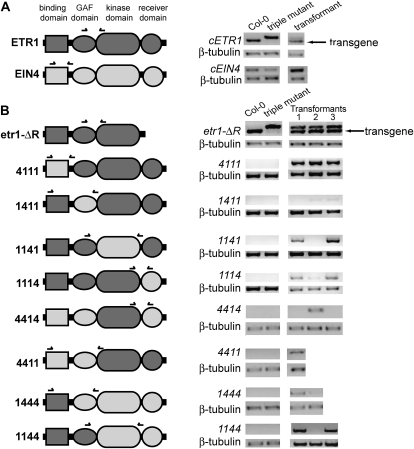
Figure 7.
Structure of ETR1-EIN4 chimeric constructs used for analyses. A, Domains of full-length ETR1 and EIN4. B, Diagrams of ETR1-EIN4 chimeric constructs used. ETR1 domains are shown dark gray and denoted with a 1 in naming the construct while EIN4 domains are light gray and denoted with a 4. All constructs were cDNA constructs under ETR1 promoter control that were transformed into the etr1-6 etr2-3 ein4-4 triple mutant background as described in the “Materials and Methods.” RNA expression levels for each transgene was analyzed using RT-PCR. The location of primers for each construct is marked above each diagram. Primers used are listed in Supplemental Table S1 Primers for the full-length (cETR1) and truncated ETR1 lacking the receiver domain (cetr1-ΔR) amplified products for both wild-type ETR1 and etr1-6. The cETR1 and cetr1-ΔR transgene transcripts ran as a smaller product (arrows) than the etr1-6 product. Primers for the chimeric receptors were designed with one primer in the EIN4 region and one in the ETR1 region of the construct so that they only amplified the transgene. Transcript levels for β-tubulin in each plant line are shown as a control.