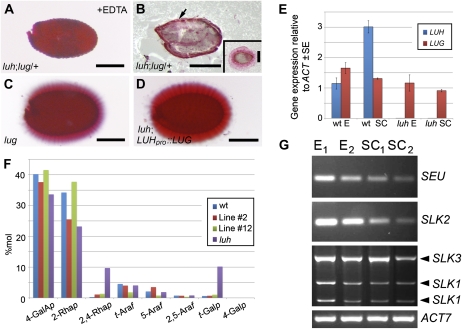
Figure 7.
Redundancy between LUH and LUG. A, Ruthenium red-stained seed obtained from a luh;lug/+ plant following a 2-h EDTA treatment. B, Ruthenium red-stained section of a wax-embedded seed obtained from a luh;lug/+ plant. Mucilage staining is indicated with the arrow. The inset shows a wild-type seed section stained with ruthenium red. C and D, Ruthenium red-stained seeds from lug mutant (C) and luh;LUHpro::LUG transgenic (D) plants displaying wild-type levels of mucilage release. Bars = 250 μm. E, qRT-PCR analysis of LUH and LUG expression in embryo (E) and seed coat (SC) samples obtained from wild-type (wt) and luh 10-dpa siliques. F, Histogram showing mol % of sugar linkages associated with the RG-I backbone and side chains present in the alkali-soluble fraction of mucilage extracted from wild-type and transgenic luh;LUHpro::LUG lines. The complete data set is presented in Supplemental Table S1. G, RT-PCR analysis of SEU, SLK1-3, and ACT7 expression in embryo (E1 and E2) and seed coat (SC1 and SC2) samples obtained from wild-type 10-dpa siliques.