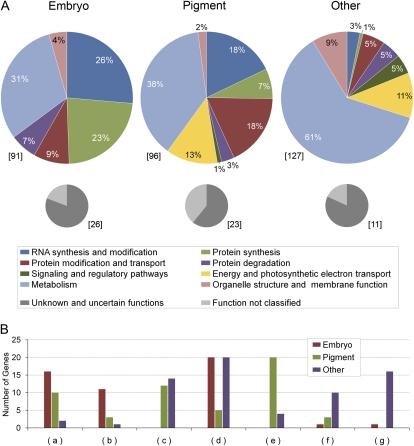
Figure 1.
Distribution of protein functions in three datasets of Arabidopsis mutants defective in chloroplast-localized proteins. Genes were classified as having an embryo-defective, pigment-defective, or other loss-of-function mutant phenotype. A, Percentages of genes with assigned (colored) and unassigned (gray) protein functions. Gene totals are indicated in brackets. B, Examples of function subclasses that differ widely between the three datasets: (a) PPR and RNA-binding proteins; (b) ribosomal proteins; (c) photosynthesis; (d) biosynthesis of amino acids, vitamins, nucleotides, and fatty acids; (e) biosynthesis of chlorophyll, carotenoids, and terpenoids; (f) biosynthesis of lipids; modification of fatty acids and lipids; (g) biosynthesis and modification of complex carbohydrates. Gene totals for each dataset are indicated. See Supplemental Table S5 for additional details.