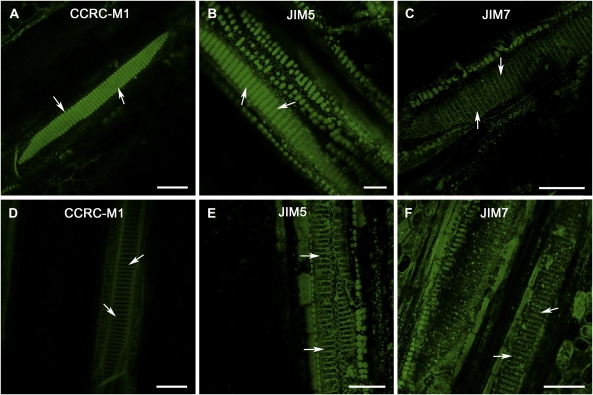
Figure 2.
Comparisons of certain pectic and hemicellulosic polysaccharide compositions in intervessel PMs of grapevine genotypes with different PD resistance. A to C, Tangential sectional views of secondary xylem tissue in PD-susceptible grapevine var. Chardonnay vines. D to F, Tangential sectional views of secondary xylem tissue in PD-resistant V. arizonica X rupestris (89-0908) vines. A, Strong fluorescent signal from intervessel PMs (arrows) incubated with CCRC-M1. B, Intervessel PMs (arrows) incubated with JIM5 had strong fluorescence. C, No fluorescent signals from intervessel PMs (arrows) incubated with JIM7. D, Signal was considerably amplified relative to that for other sections to pick up very weak autofluorescence to distinguish vessel lateral walls. Even under this condition, fluorescent signal from intervessel PMs (arrows) incubated with CCRC-M1 were below the detectable level. E, Signal was amplified as in D to make vessels’ secondary wall regions visible. Even then, there was no detectable fluorescent signal from intervessel PMs (arrows) incubated with JIM5. F, Weak fluorescent signal from intervessel PMs (arrows). Bar in each section equals 50 μm.