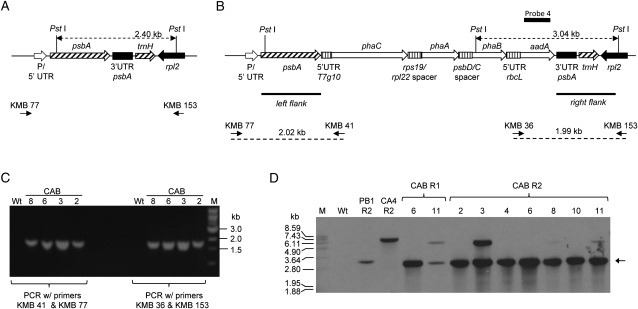
Figure 1.
Integration of pCAB at the psbA locus. A and B, Diagrams illustrating the genetic arrangement of the wild-type psbA locus (A) and the expected genetic arrangement of the psbA locus after plastid transformation with pCAB (B). Binding sites of PCR primers used to verify correct insertion of the transgenic DNA behind the psbA coding sequence (KMB 77, KMB 41, KMB 36, and KMB 153) are shown in B along with the size of each predicted PCR product. C, Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products demonstrating correct integration of the transgenic DNA. M, Marker; Wt, wild-type plant. Samples 2, 3, 6, and 8 are derived from CAB plant lines 2, 3, 6, and 8 in the R2 regeneration cycle (for explanation of regeneration cycles, see Fig. 3). D, Southern blot of PstI-digested genomic DNA from transplastomic and wild-type lines probed with probe 4, a DNA fragment with homology to the aadA gene. Genomic DNA was isolated from the following lines: Wt, the wild type; PB1 R2, line obtained after plastid transformation of pUCaadA in the R2 regeneration cycle; CA 4 R2, line obtained after plastid transformation of pCA in the R2 regeneration cycle; CAB R1 lines 6 and 11, lines obtained after plastid transformation of plasmid pCAB in the R1 regeneration cycle; CAB R2 lines 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 11, lines obtained after plastid transformation of pCAB in the R2 regeneration cycle. The arrow shows the expected 3.04-kb band for the expected integration event for CAB lines.