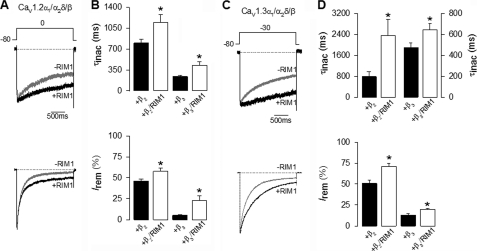
FIGURE 2.
RIM1 changes the inactivation kinetics of recombinant L-type CaV channels. A, representative whole cell currents recorded in HEK-293 cells expressing CaV1.2α1/CaVα2δ-1 channels, with CaVβ2 (upper traces) or CaVβ3 (lower traces) in the absence and presence (black and gray traces, respectively) of RIM1. Peak amplitude of the currents before and after RIM1 co-expression was normalized for comparison. Currents were elicited by 2-s depolarizing pulses from a Vh of −80 to 0 mV. B, comparison of time constant of inactivation (top) and percentage of current remaining at the end of the 2-s voltage step (Irem) in cells expressing CaV1.2α1/CaVα2δ-1/CaVβ channels in the absence (solid bars) or presence (open bars) of RIM1. C, representative current traces recorded in HEK-293 cells expressing CaV1.3α1/CaVα2δ-1 channels together with CaVβ2 or CaVβ3 in the absence and presence of RIM1 (as in A). Currents were evoked by 2-s depolarizing pulses from a Vh of −80 to −30 mV. D, comparison of time constant of inactivation (top) and percentage of current remaining at the end of the voltage step in cells expressing CaV1.3α1/CaVα2δ-1/CaVβ channels in the absence or presence of RIM1 (as in B). *, significant differences (p < 0.05) compared with control without RIM1. Error bars, S.E.