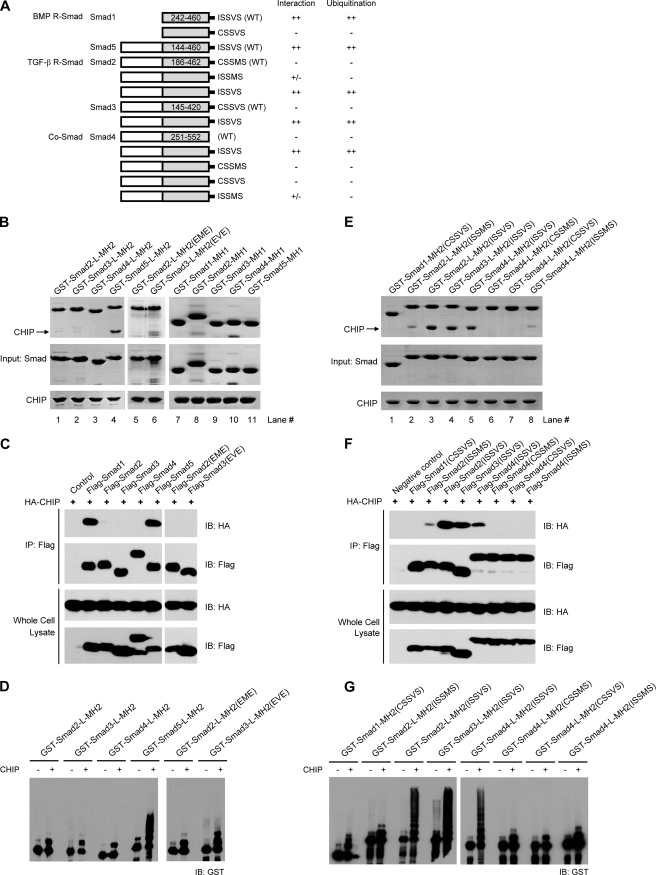
FIGURE 6.
CHIP specifically targets Smad1/5 but not Smad2/3/4. A, shown are schematic diagrams of Smad mutants. The results of the CHIP binding and ubiquitination assays are summarized. B, interactions between the MH1 and MH2 domains of Smad2, -3, -4, and -5 and CHIP. The GST-mediated pulldown assays were carried out using full-length CHIP and various GST-tagged Smad proteins as indicated. C, co-immunoprecipitation (IP) assays detecting the interactions between full-length Smad proteins and CHIP are shown. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with 2 μg of FLAG-Smad1–5 and 1 μg of HA-CHIP plasmids as indicated. After immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody for Smad proteins, immunoblotting (IB) was carried out using anti-HA and anti-FLAG antibodies for CHIP and Smad, respectively. D, CHIP-mediated ubiquitination of Smad2, -3, -4, and -5 proteins is shown. Pseudophosphorylation of Smad2/3 exhibited little if any effect on both interaction and ubiquitination. E, interactions between the chimeric Smad-MH2 fragments and CHIP analyzed by GST-mediated pulldown assay are shown. F, interactions between full-length Smad proteins and CHIP determined by coimmunoprecipitation analyses are shown. G, CHIP-mediated ubiquitination of chimeric Smad proteins correlated precisely with their interaction abilities.