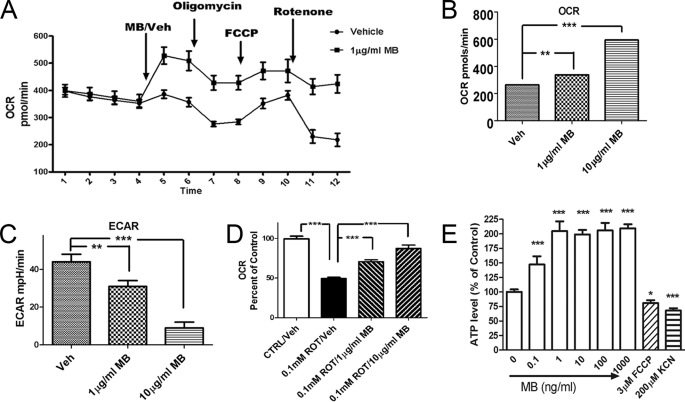
FIGURE 1.
MB improves mitochondrial respiration and reduces anaerobic glycolysis. A, effects of MB on cellular oxygen consumption in HT-22 cells. Cellular oxygen consumption was monitored with sequential injection of MB/vehicle, oligomycin, FCCP, and rotenone. The vehicle- and MB-treated groups had a significant difference in OCR at all time points (n = 5). B–D, OCR (mitochondrial respiration) and ECAR were monitored with similar sequential treatment in A after 4-h MB/vehicle incubation at the indicated concentration. MB induced a significant dose-dependent increase in OCR (B), a dose-dependent decrease in ECAR (C), and a dose-dependent attenuation of rotenone-induced OCR inhibition (D) (n = 5). E, effects of MB on cellular ATP levels. Shown is a representative assay of intracellular ATP level in HT22 cells treated with the indicated concentration of MB. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001. Error bars, S.E.