Figure 2.
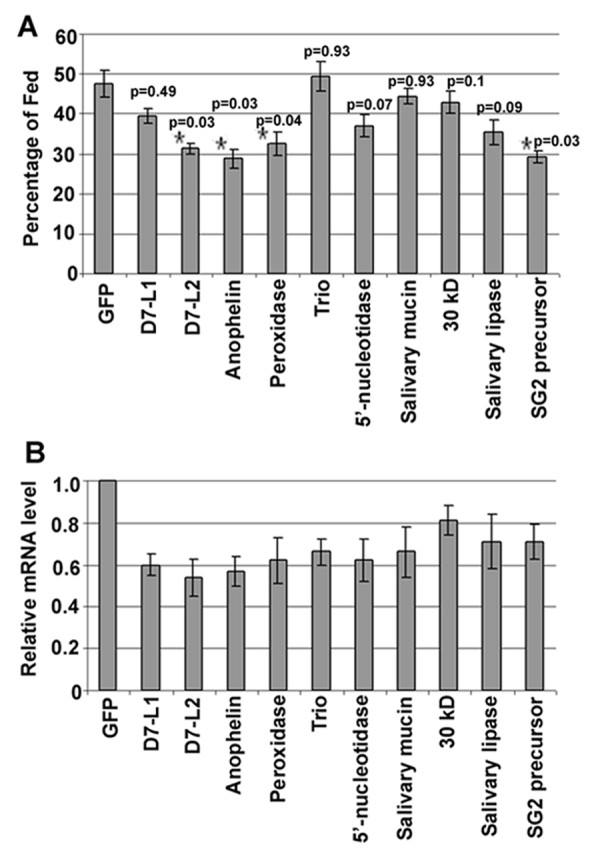
Implication of salivary gland genes in blood-feeding capacity. A. The percentage of gene-silenced mosquitoes that fed on a mouse after gene-specific silencing through RNAi compared to the GFP dsRNA injected control mosquitoes. Data were pooled from six replicates of 25 mosquitoes each. Genes displaying significant capacity to alter blood feeding propensity upon silencing are indicated with an asterisk, and the p-values are shown for each gene (from the Mann-Whitney test). The error bars indicate the standard error. B. Determination of RNAi-mediated gene silencing efficiency, by qRT-PCR at 4 days after dsRNA injection. The cDNA templates were normalized using the AgS7 gene specific primers. The graph shows the relative transcript abundance of each gene after knockdown, as compared to its abundance in the GFP dsRNA-treated control mosquitoes (set to 1.0). The error bars indicate the standard error.
