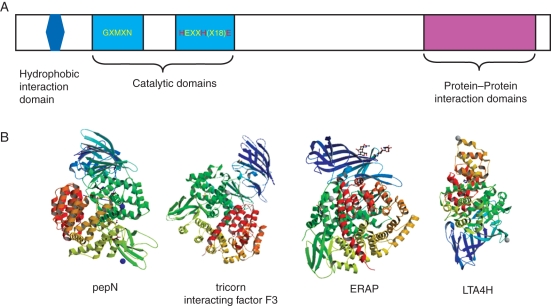
Fig. 1.
Organization and structures of M1 metallopeptidases. (A) Pictogram of an M1 metalloprotease showing the enzymatic domains (light blue), hydrophobic domain (dark blue) and protein–protein interaction domains (magenta). The zinc-binding amino acids are highlighted in red. (B) Crystal structures (from the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics Protein Database) of M1 metallopeptidases: Escherichia coli aminopeptidase N (pepN) in complex with phenylalanine (3B34) (Addlagatta et al., 2008); tricorn interacting factor F3 from Thermoplasma acidophilum (1Z5H ) (Kyrieleis et al., 2005); soluble domain of human endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 ERAP1 (2XDT) (Vollmar et al., 2010); LTA4H in complex with Arg-Ala-Arg substrate (3B7T) (Tholander et al., 2008). The zinc ion is represented by a blue (pepN, ERAP) or grey (tricorn F3, LTA4H) sphere.