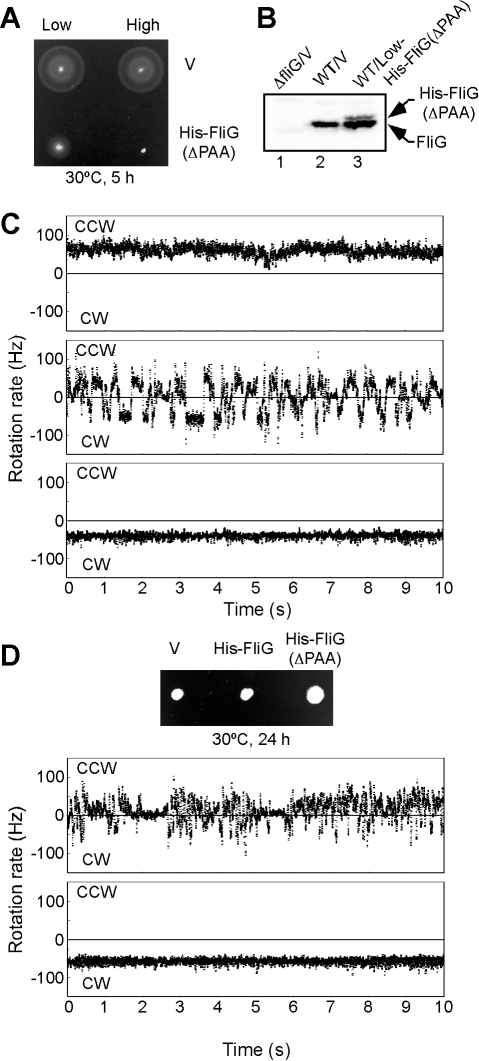
Figure 1. Dominant-negative effect of FliG(ΔPAA) on motility of wild-type cells.
(A) Motility of SJW1103 cells (wild-type) transformed with pET19b (indicated as Low-V), pTrc99A (indicated as High-V), pGMK4000 (pET19b/His-FliG(ΔPAA), indicated as Low-FliG(ΔPAA)), and pGMM4500 (pTrc99A/His-FliG(ΔPAA), indicated as High-FliG(ΔPAA)) in semi-solid agar plates. (B) Expression levels of FliG and His-FliG(ΔPAA). Immunoblotting, using polyclonal anti-FliG antibody, of whole cell proteins. Lane 1, MKM1/pET19b (indicated as ΔfliG/V); lane 2, SJW1103/pET19b (indicated as WT/V); lane 3, SJW1103/pGMK4000 (indicated as WT/Low-His-FliG(ΔPAA)). Arrows indicate positions of FliG and His-FliG(ΔPAA). (C) Measurement of CCW and CW rotation of the flagellar motor by bead assays. We used SJW46 (fliC(Δ204–292)) as a host because it produces flagellar motors with the sticky flagellar filaments, which are easily labeled with polystyrene beads. CCW, counterclockwise rotation; CW, clockwise rotation. Upper panel: SJW46 carrying pET19b. Middle panel: SJW46 carrying pGMK4000. Bottom panel: SJW46 carrying pGMM4500. (D) Effect of FliG(ΔPAA) on motility of a ΔcheA-Z mutant. Upper panel: Motility of SJW3076 (ΔcheA-Z) transformed with pET19b, pGMK3000 (pET19b/His-FliG), or pGMK4000 in semi-solid agar. Middle panel: measurement of CCW and CW rotation of the flagellar motor of MM3076iC/pGMK4000. Bottom panel: measurement of CCW and CW rotation of the flagellar motor of MM3076iC/pGMM4500.