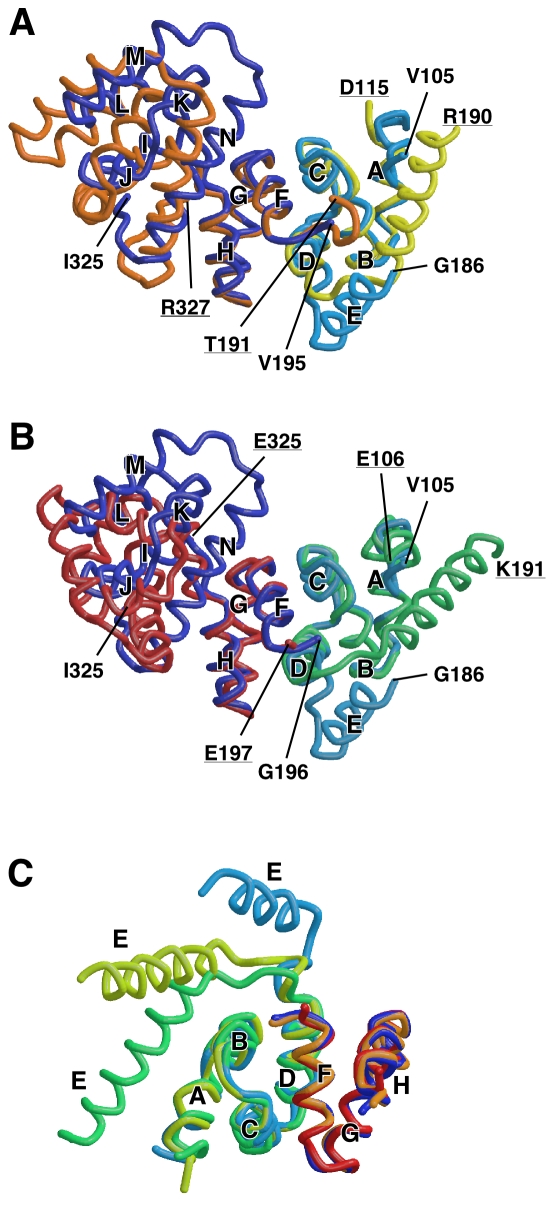
Figure 4. Structural comparison of the FliGM-FliGC unit.
(A) Comparison of Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV) and wild-type Tm-FliGMC (PDB code 1lkv). A FliGM-FliGC unit of wild-type Tm-FliGMC, which is composed of FliGM of one subunit and FliGC of the neighboring subunit related by 2-fold crystallographic symmetry, is superimposed onto Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV) using Cα atoms of V117-L165 and G196-F236 for least-square fitting. FliGM with helix E and FliGC of Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV) are colored cyan and blue, respectively. FliGM with helix E and FliGC of wild-type Tm-FliGMC are yellow and orange, respectively. (B) Comparison of Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV) with Aa-FliG (PDB code 3hjl). A FliGM-FliGC unit of Aa-FliG, which is composed of FliGM of one molecule and FliGC of the neighboring molecule related by 2-fold crystallographic symmetry, is superimposed onto Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV) using Cα atoms of the same region used in (A). Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV) is shown in the same color as in (A), and FliGM and FliGC of Aa-FliGMC are shown in green and red, respectively. (C) Comparison of the orientation of helix E. The FliGM-FliGCN units of wild-type Tm-FliGMC and wild-type Aa-FliGMC are superimposed on Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV). The models are shown in the same colors used in (A) and (B).