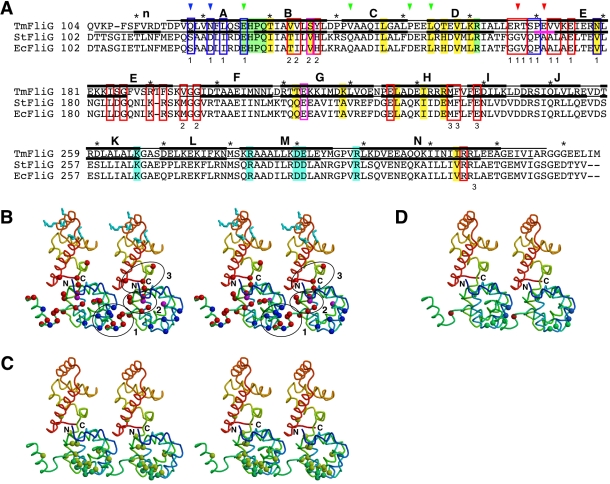
Figure 6. A plausible model for arrangement of FliG subunits in the rotor.
(A) A primary sequence alignment of FliGMC from T. maritima (TmFliG), Salmonella Typhimurium (StFliG), and Escherichia coli (EcFliG). The regions involved in the structure models of Tm-FliGMC and Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV) are shown in black bars above and below the Tm-FliG sequence, respectively. The α-helical regions are indicated by thick bars labeled with the same codes used in Figure 3. The region of the three-amino-acid deletion is shown by the magenta bar. The charged residues essential for the motor function are highlighted in cyan. The EHPQR motif is highlighted in green, and the other residues thought to be related to FliM-binding are shaded highlighted in yellow [21],[37]. In vivo cross-linking experiments using various Cys-substitution mutants of FliGM have shown that residues indicated by blue arrows are located near the residues indicated by red ones. The Cys-substitution sites that did not show any cross-linked products are indicated by green arrows [22]. Blue and red boxes indicate point mutations that bias the motor rotation to CCW and CW, respectively [38]. The residues within magenta boxes can give rise to CCW or CW-biased mutants, depending on the substitutions. The numbers under the boxes represent the number of the cluster to which the indicated residues belong. (B–D) Mapping of various mutation sites identified in previous studies on the model of Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV). A stereo pair of the Tm-FliGMC(ΔPEV) subunits, color coded from blue to red going from the N- to the C-terminus, is shown in each panel. (B–C) Stereo diagram of the subunit arrangement model. (B) The charged residues essential for motor function are shown in stick representation colored in cyan. Residues at which substitutions affect the direction of motor rotation are indicated by balls: blue, CCW motor bias; red, CW motor bias; magenta, CCW or CW motor bias, depending on the substitution. The clusters of residues targeted by mutations are surrounded by ellipsoids and labeled (1, 2, and 3). (C) Residues involved in FliM binding are indicated by balls: yellow, residues at which substitutions decrease FliM binding; green, the EHPQR motif. (D) Residues substituted with Cys for in vivo cross-linking experiments are shown by balls. Residues indicated in blue cross-linked to residues indicated in red. Residues that produced no cross-linking products are colored in green.