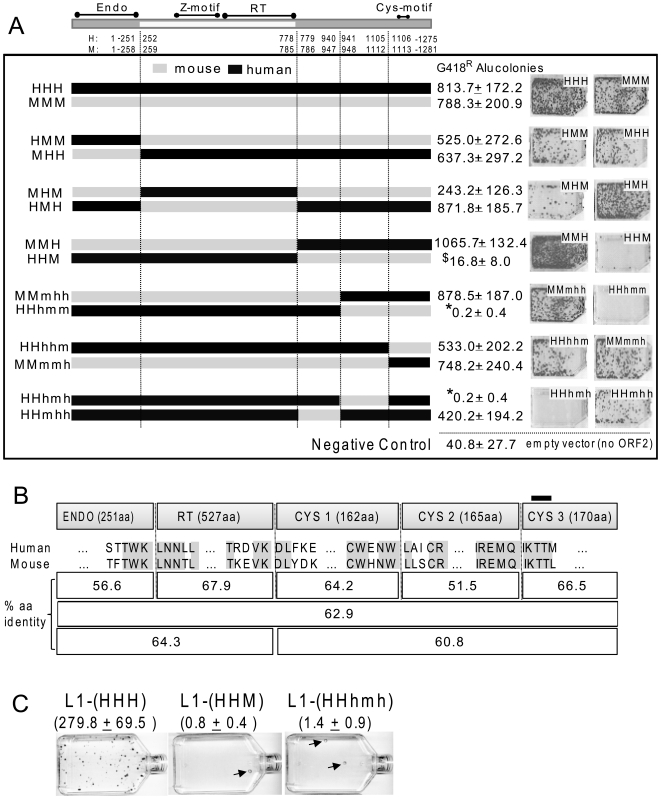
Figure 3. L1 ORF2p human-mouse chimera.
A. Chimera breakpoint schematic of chimeric ORF2s and their ability to drive Alu retrotransposition in trans . A schematic for the L1 ORF2 protein with its three recognized domains, endonuclease (endo), reverse transcriptase (RT) and the ill-defined 3′ region containing the cysteine-rich motif (cys), subdivided into three parts. The amino acid positions flanking the selected break points are indicated for human and mouse ORF2s. The constructs are named using 3 capital letters, each representing a domain: H for human and M for the mouse portions, where HHH and MMM represent complete human and mouse ORF2 proteins, respectively. In constructs where the cys-domain was further subdivided, the third capital H or M was replaced with three lowercase h or m letters, indicating the subdivision of the cys-domain. HeLa cells were co-transfected with a tagged Alu and the different chimeric ORF2 expression constructs. Results from the Alu retrotransposition assay average colony counts with standard deviation, along with images of representative colony assays, are shown to the right of each of the construct schematics. Averages are derived from six replicate experiments. Assay results using an empty vector (i.e., no ORF2 supplied in trans) show the average number of background colonies of Alu retrotransposition events that are inferred to be derived from endogenously expressed ORF2p in human HeLa cells. An asterisk (*) represents significant difference from empty vector, p<0.01, two-tailed two sample T-test; $ represents not significantly different from empty vector. B. Chimera breakpoints and amino acid conservation between human and mouse L1 ORF2 proteins. ORF2p chimera breakpoints and numbers of amino acids (aa, taken from the human ORF2p) are shown in the first row. The next two rows show the five amino acid residues on each side of the breakpoints (ORF2s from human L1RP and mouse L1spa). Conserved human and mouse residues are highlighted. The three bottom rows show average amino acid conservation between human and mouse proteins for the indicated ORF2p segments. The location of the cys-motif is shown at the top as a dark bar. C. Tagged LI constructs with substituted chimeric ORF2p HHM and HHhmh in place of the parental ORF2 significantly limit L1 cis retrotransposition capability. L1 retrotransposition assay results in HeLa cells using the parental human L1 construct (pBS-L1PA1CH mneo, shown as L1-HHH) and the same construct with substituted chimeric ORF2, as indicated. The observed G418R foci (mean ± standard deviation) are indicated for three repeats of the experiment, with the L1 chimeras showing significantly fewer colonies than the parental L1 (200–350 fold difference; p<0.0001, one-tailed two sample T-test). A representative of the retrotransposition results is shown with arrows indicating infrequent colonies from the chimeric L1 transfections.