Figure 1.
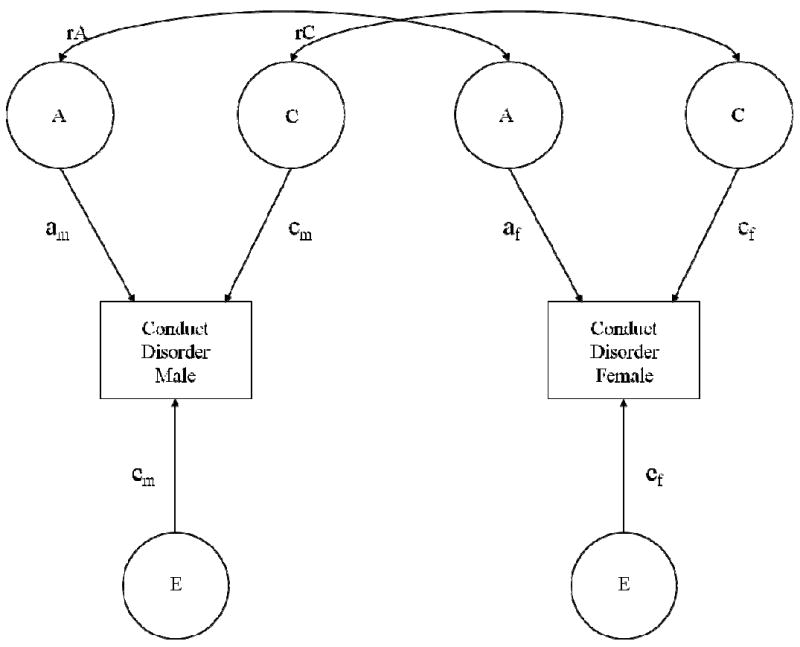
Univariate sex-limitation model for childhood conduct disorder. The magnitude of additive genetic (A), shared environmental (C), and non-shared environmental (E) influences may differ for males and females (am ≠ af, cm ≠ cf, ef ≠ em), and/or the genetic (rA) or shared-environmental (rC) correlation among opposite-sex twins may fall below the expected genetic (.50) and shared-environmental (1) correlations for same-sex DZ twins. The same univariate sex-limitation model was used for adult antisocial behavior.
