Figure 5.
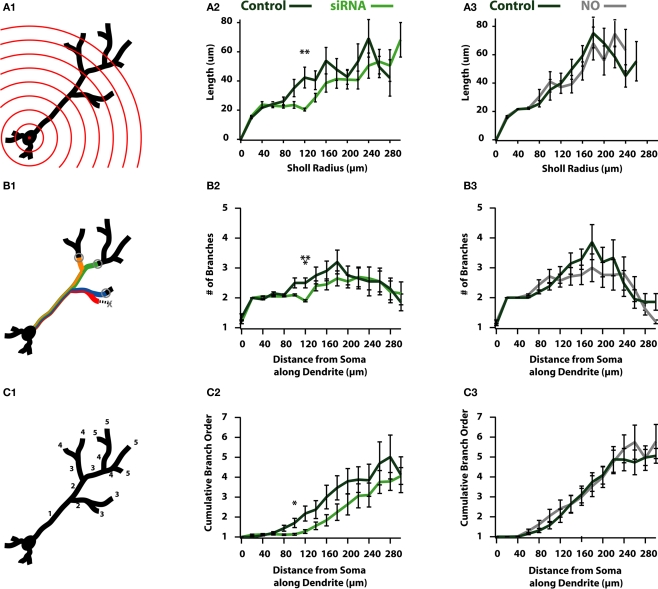
Reductions in activity reduce the overall complexity of newborn ABNs. (A1) Classical Sholl analysis with radii increasing in 20 μm increments. Sholl analysis measures apical dendrite length within each sphere plotted against radius from soma. (A2) siRNA knock-down cells show a significant reduction in length in proximal-intermediate distances from soma (at 120 μm: p < 0.01, n = 20). (A3) NO cells show no significant differences in Sholl analysis. (B1) Modified Sholl analysis of branch intersections. Modified Sholl analysis represents the number of branches at a fixed distance along the apical dendrite (not counting terminated branches). (B2) siRNA knock-down cells show a significant reduction in the number of branches at proximal-intermediate distances from soma (at 120 μm: p < 0.001, n = 20). (B3) NO cells show no significant differences in modified Sholl analysis. (C1) Cumulative branch order along length of apical dendrite. Plotted as the cumulative branch order (where branch order increments by one following bifurcation) vs. distance from soma along apical dendrite length. (C2) siRNA knock-down cells show a significant reduction in cumulative branch order at proximal-intermediate distance from soma (at 100 μm: p < 0.05, n = 20). (C3) NO cells show no differences in cumulative branch order.