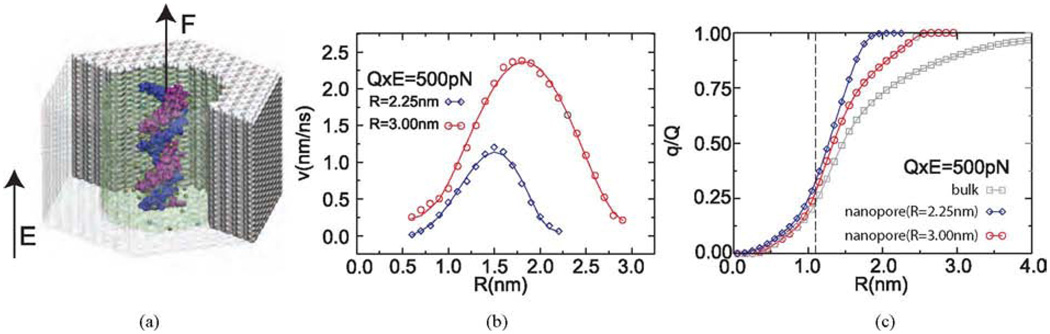
Fig. 2.
Analyzing the forces on DNA in a nanopore. (a) All-atom model of DNA solvated in 100 mM KCl electrolyte in a nanopore in a nitride membrane. DNA is simulated under simultaneous actions of force F, which is a harmonic spring used to measure the net force on DNA and an external electric field E. (b) Pattern of the electro-osmotic flow between DNA and the nanopore surface. The diameter of DNA is ∼2.4 nm. (c) Net charge of the electrolyte within the distance R from the central axis of the DNA, i.e., q(R) = Σ qion (r < R). q is the charge of the bare DNA. The dashed line indicates the position of the DNA surface. Figure adapted from Ref. [44].