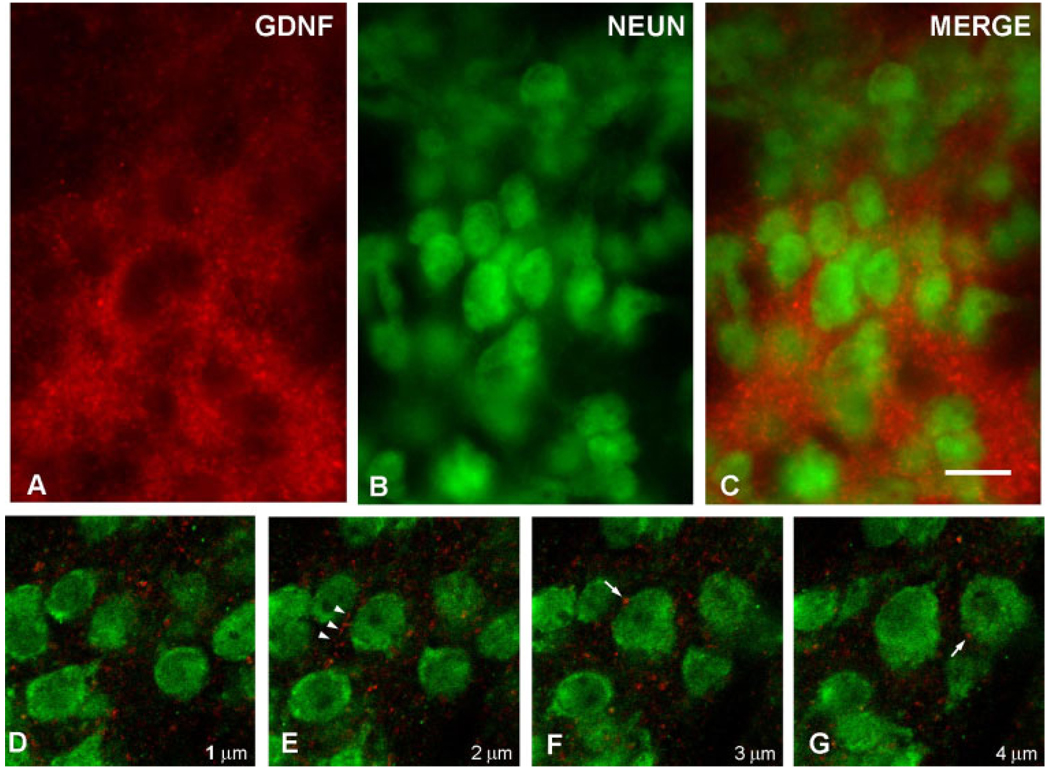
Fig. 4.
Immunofluorescence labeling of GDNF and NeuN. A: A GDNF-positive striatal patch is identified by red AlexaFluor594 staining at PND6. Punctate and fibrillar staining is observed. B: Striatal neurons are identified by NeuN staining using a fluorescein label. C: A merged image reveals the NeuN-positive neurons enmeshed within the GDNF-positive fibrillar network. The extensive, overlapping GDNF fiber staining in this section observed by epifluorescence obscures any possible underlying GDNF staining within cytoplasm. Therefore, confocal analysis of serial optical sections was performed, as shown in consecutive sections D–G. These sections reveal fibrillar GDNF staining (arrowheads in E) and diffuse punctuate staining, some of it juxtaposed to neuronal cell bodies (arrows in F, G). No GDNF staining was observed in the cytoplasm of any NeuN-positive neurons in striosomes. The micron measurements in the lower right corner of panels D–G represent the Z-axis distances above the plane shown in D, arbitrarily defined as the initial plane at 1 µm. Scale bar = 10 µm in C (applies to A–G).