Fig. 2.
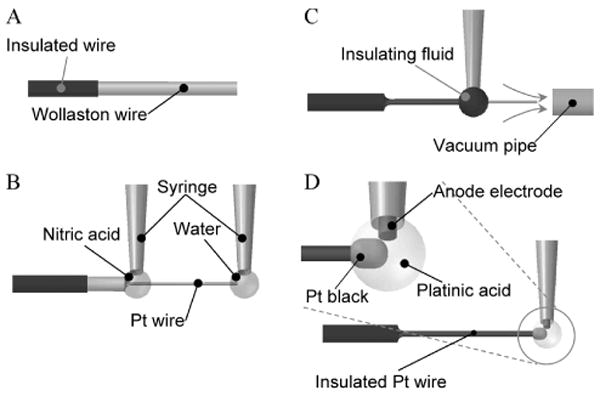
Fabrication of the nanowire electrode.
(A) Preparation. A tip of a Wollaston wire, i.e., a submicron Pt wire covered with Ag 40 μm in thickness, was insulated. The wire tip of 1 mm was left uninsulated for further processing. (B) Etching. The Ag-coated Pt nanowire was dipped in a drop of nitric acid, and the Ag topcoat was removed to expose the Pt wire. During this process a drop of water held the tip of the wire to keep the wire straight. (C) Insulation. The Pt wire was dipped in a drop of insulating fluid, and the drop moved toward the wire tip. The insulation fluid was baked in a laminar airflow holding the wire. (D) Platinization. A drop of platinic acid was applied to the wire tip to plate it with platinum black.
