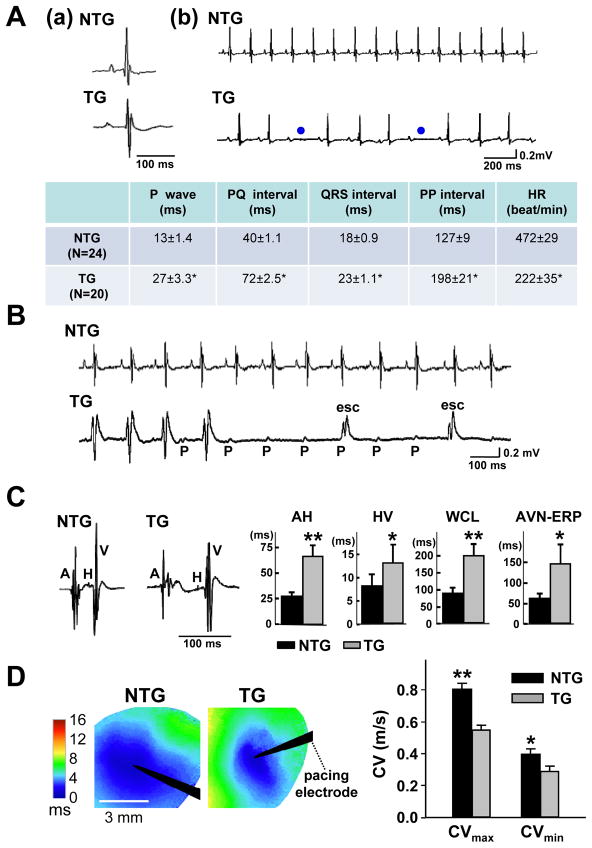
Figure 2.
Adult αMyHC-FKBP12 mice exhibit abnormal cardiac conduction and rhythm. A, (a and b) Representative surface ECGs obtained from a NTG and a TG mouse, respectively. The ECG from the TG mouse shows longer PP intervals and 2nd degree AV block (blue dots). Table summarizes the ECG parameters obtained in TG (n=20) and NTG mice (n=24); *P<0.001 for TG versus NTG. B, Representative ambulatory ECG tracings in conscious NTG and TG mice. Transient complete AV block with escape rhythm (esc) was observed in the TG mouse. C, Electrophysiological analysis in Langendorff-perfused hearts. The left two panels show representative intracardiac electrograms recorded in an NTG and TG heart, respectively. Bar graphs show that the means for the AH (atrium-His) and HV (His-ventricular) intervals, Wenckebach cycle length (WCL), and effective refractory period of the AV node (AVN-ERP) were significantly prolonged in TG hearts (TG: n=9; NTG: n=8); *P<0.05; **P<0.01 for TG versus NTG. D, Left ventricular epicardial conduction velocities (CVs) (TG: n=7; NTG: n=7). Left panels illustrate representative color-coded isochronal maps during unipolar pacing. Black arrow heads denote positions of stimulating electrodes. The mean CVs in TG hearts were significantly smaller in both the longitudinal and transverse direction compared with the NTG hearts. *P<0.05; **P<0.01.