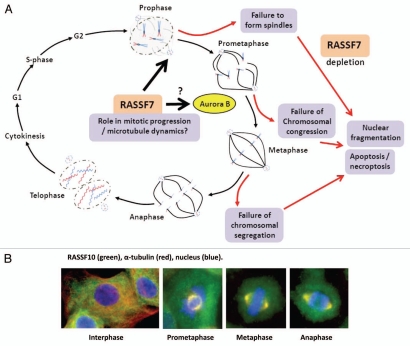
Figure 2.
Emerging molecular functions of RASSF7 and RASSF10. (A) During mitosis RASSF7 localizes at centrosomes and with associated microtubules in both Xenopus and human cells. Loss of RASSF7, by RNAi-mediated knockdown, results in spindle defects and failure of chromosome alignment/segregation leading to mitotic catastrophe, DNA degradation and apoptosis. The functional mechanics of RASSF7 are unclear but recent evidence suggests a regulatory role in Aurora B kinase activation and microtubule attachment during the formation of the mitotic spindles in the early stages of mitosis.4,9 (B) The latest member of the N-terminal RASSF family, RASSF10, has been shown to display a cell cycle-dependent distribution, relocating from the cytoplasm into the nucleus at the start of the mitotic cycle where it concentrates at developing centrosomes and associated microtubules.45