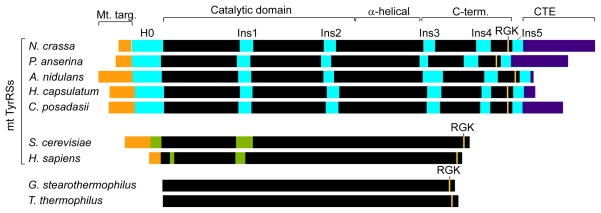
Figure 1.
Comparison of splicing-active Pezizomycotina mt TyrRSs with non-splicing bacterial and mt TyrRSs. The Pezizomycotina mt TyrRSs are distinguished by a series of insertions, including an α-helical N-terminal extension H0, Ins1 and Ins2 in the catalytic domain, and Ins3–5 in the C-terminal domain. Other fungal mt TyrRSs contain an Ins1 and sporadic insertions at the positions of Ins2 and 3, but with no significant sequence similarity to the Pezizomycotina mt TyrRS insertions. Black, regions of the canonical TyrRSs fold; orange, mt targeting sequences; cyan, Pezizomycotina-specific insertions; violet, C-terminal extensions (CTE); green, insertions relative to bacterial sequences in the yeast and human mt TyrRSs.