Abstract
We have prepared several novel phosphoramidites and have synthesised oligonucleotides incorporating them internally. The presence of these residues in an oligonucleotide template presents an impossible barrier to primed synthesis by Taq DNA polymerase. When extended as polymerase chain reaction products, these oligonucleotides no longer serve as templates for the polymerase beyond the insertion sites of the modified intermediates, thereby producing single-stranded tails on amplification products. These tails can then be used for solid phase capture and colorimetric detection of PCR products.
Full text
PDF


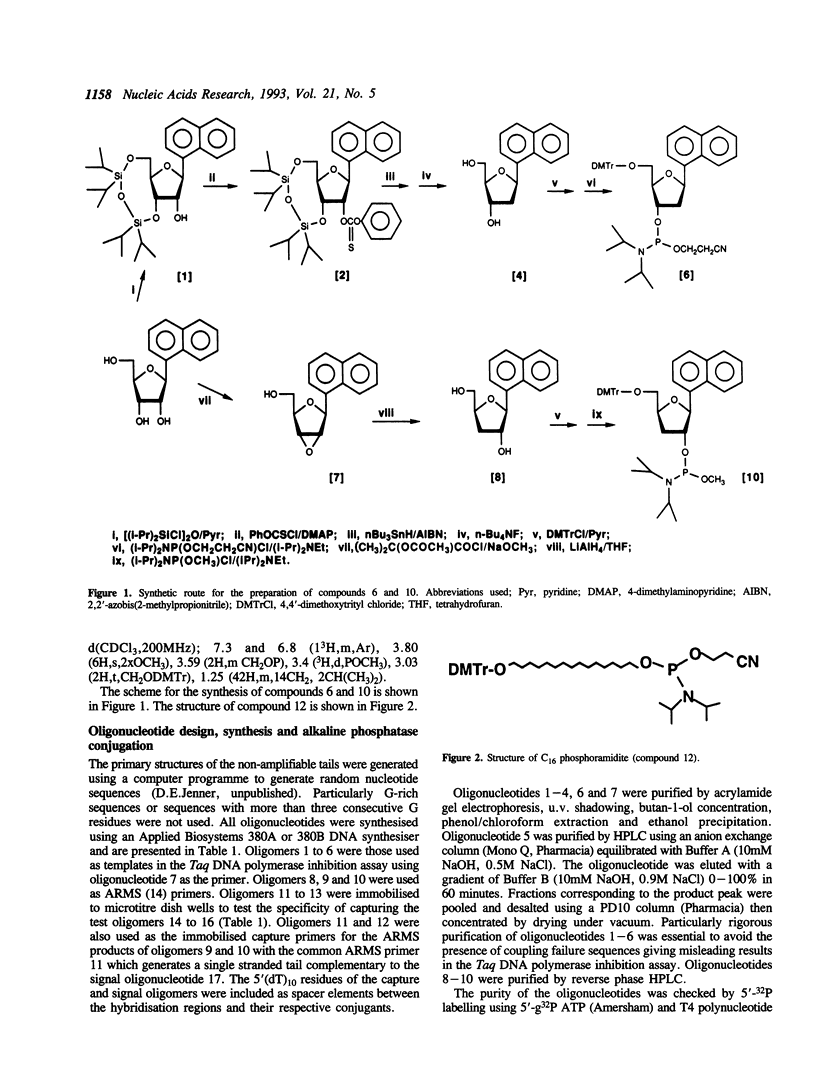



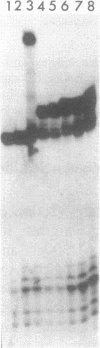
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen N., Winter V., Petersen K. B., Koch J., Kølvraa S., Rüdiger N., Heinsvig E. M., Bolund L. Detection of point mutations in amplified single copy genes by biotin-labelled oligonucleotides: diagnosis of variants of alpha-1-antitrypsin. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 Jun 30;182(2):151–164. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R. G., Ochman H. Production of single-stranded DNA templates by exonuclease digestion following the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5865–5865. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlston R. S., Snowden C., Green F., Alberti K. G., Humphries S. E. Apolipoprotein (apo) E genotypes by polymerase chain reaction and allele-specific oligonucleotide probes: no detectable linkage disequilibrium between apo E and apo CII. Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;83(4):364–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00291382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. H., Huang D. P., Shih J. W., Manak M. M. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum by polymerase chain reaction amplification and microtiter sandwich hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1411–1416. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1411-1416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Smith D. B., Foote S. J., Samaras N., Peterson M. G. Colorimetric detection of specific DNA segments amplified by polymerase chain reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2423–2427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirmaier C., Holten D., Bylina E. J., Youvan D. C. Electron transfer in a genetically modified bacterial reaction center containing a heterodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7562–7566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleppe K., Ohtsuka E., Kleppe R., Molineux I., Khorana H. G. Studies on polynucleotides. XCVI. Repair replications of short synthetic DNA's as catalyzed by DNA polymerases. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):341–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKellar C., Graham D., Will D. W., Burgess S., Brown T. Synthesis and physical properties of anti-HIV antisense oligonucleotides bearing terminal lipophilic groups. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3411–3417. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. R., Graham A., Heptinstall L. E., Powell S. J., Summers C., Kalsheker N., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2503–2516. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L., Weiss S. J., Fisher P. A. Recognition and binding of template-primers containing defined abasic sites by Drosophila DNA polymerase alpha holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13018–13023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall S. K., Eritja R., Kaplan B. E., Petruska J., Goodman M. F. Nucleotide insertion kinetics opposite abasic lesions in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6864–6870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Running J. A., Urdea M. S. A procedure for productive coupling of synthetic oligonucleotides to polystyrene microtiter wells for hybridization capture. Biotechniques. 1990 Mar;8(3):276–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. F., Greenberg S., Moffatt J. G. Reactions of 2-acyloxyisobutyryl halides with nucleosides. II. Reactions of adenosine. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Jun 13;95(12):4025–4030. doi: 10.1021/ja00793a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Chang C. A., Levenson C. H., Warren T. C., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Erlich H. A. Diagnosis of sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia with enzymatically amplified DNA and nonradioactive allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):537–541. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Walsh P. S., Levenson C. H., Erlich H. A. Genetic analysis of amplified DNA with immobilized sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6230–6234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauvaigo S., Fouqué B., Roget A., Livache T., Bazin H., Chypre C., Téoule R. Fast solid support detection of PCR amplified viral DNA sequences using radioiodinated or hapten labelled primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3175–3183. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Chang C. N., Johnson F., Will S., Grollman A. P. Oligodeoxynucleotides containing synthetic abasic sites. Model substrates for DNA polymerases and apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10171–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg J., Lundeberg J., Hultman T., Uhlén M. General colorimetric method for DNA diagnostics allowing direct solid-phase genomic sequencing of the positive samples. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6569–6573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]