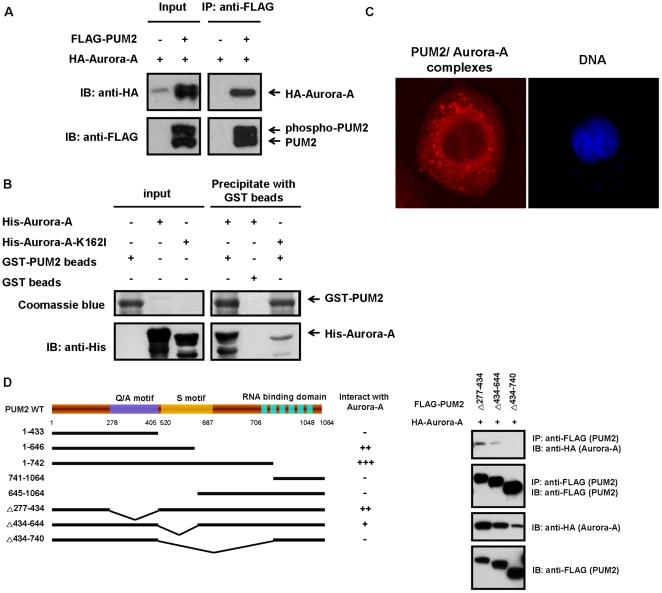
Figure 2. PUM2 interacts physically with Aurora-A, and the S motifs, not the PUM-HD motif, of PUM2 are required for this interaction.
(A) PUM2 forms a complex with Aurora-A in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-tagged Aurora-A, either alone or in combination with FLAG-tagged PUM2. The samples were immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody and then immunoblotted with an anti-HA antibody to detect Aurora-A. (B) Recombinant Aurora-A and PUM2 form a complex as determined using a GST pull down assay. Purified GST-PUM2 fusion protein or a control (GST immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads) was incubated with purified His-tagged Aurora-A or kinase-inactive mutant protein (Aurora-A-K162I). Bead-bound proteins were immunoblotted against an anti-His antibody, and the gel was also stained with coomassie blue. His-tagged Aurora-A and kinase-inactive mutant protein alone are also shown. (C) Detection of endogenous PUM2-Aurora-A complexes by in situ proximity ligation assay (PLA). Complexes between endogenous PUM2 and Aurora-A were visualized by staining CL1–5 cells with anti-PUM2 and anti-Aurora-A antibodies. Each red dot represented an interaction detected by the PLA assay. DNA was stained with DAPI (blue) and the cells were visualized using confocal fluorescence microscopy. (D) The S motifs of PUM2 are required for the interaction with Aurora-A. Five PUM2 truncation mutants and three deleted PUM2 mutants were generated based on the putative domains present in PUM2. HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-tagged Aurora-A and various FLAG-tagged PUM2 mutants. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody and then immunoblotted with an anti-HA antibody to detect Aurora-A.