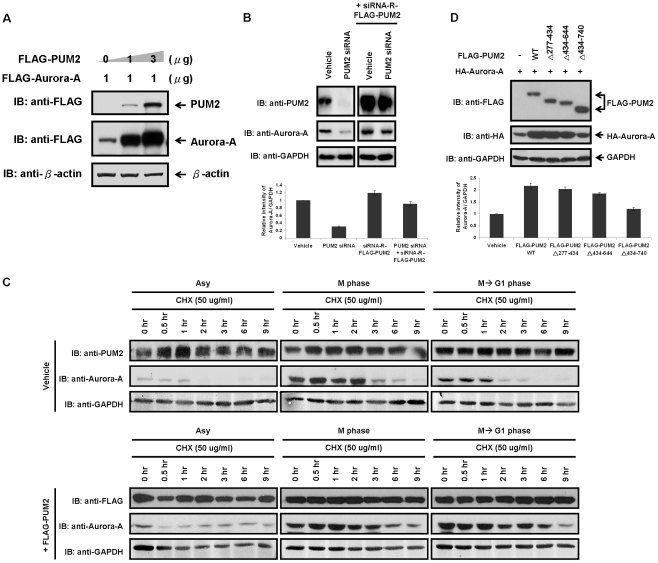
Figure 3. PUM2 is able to enhance the protein stability of Aurora-A, which is indispensable for the interaction between Aurora-A and PUM2.
(A) The stability of Aurora-A is regulated by PUM2. HEK293T cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged Aurora-A, either alone or with different amounts of FLAG-tagged PUM2. The cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (B) Knock-down of PUM2 results in the down-regulation of both PUM2 and Aurora-A. HEK293T cells were transfected with PUM2 specific siRNA or in combination with siRNA-R-FLAG-PUM2 and the effect of steady-state protein level of Aurora-A was determined using immunoblotting analysis. The relative intensity of protein bands on immunoblotting were quantified and normalized to GAPDH. (C) PUM2 protects Aurora-A from protein degradation when the cells exit from mitosis. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with an empty vector or with FLAG-tagged PUM2. 24 hrs after transfection, the cells were synchronized in mitosis by nocodazole. For the collection of cells exiting from M phase, the cells were released into the cell cycle progression by removing the mitosis-synchronizing reagent and subsequently incubated with fresh medium containing cycloheximide, which blocks de novo protein synthesis. For the collection of M phase cells, the cells were also treated with nocodazole but this mitosis-synchronizing reagent was not removed when incubating with cycloheximide-containing medium. At the indicated time points, the cells were harvested and the lysates were immunoblotted with anti-PUM2, anti-FLAG, anti-Aurora-A and anti-GAPDH antibodies. Asynchronously (Asy) growing cells were analyzed in parallel. (D) Overexpression of PUM2 mutant, which failed to interact with Aurora-A, leads to the destabilization of this kinase.