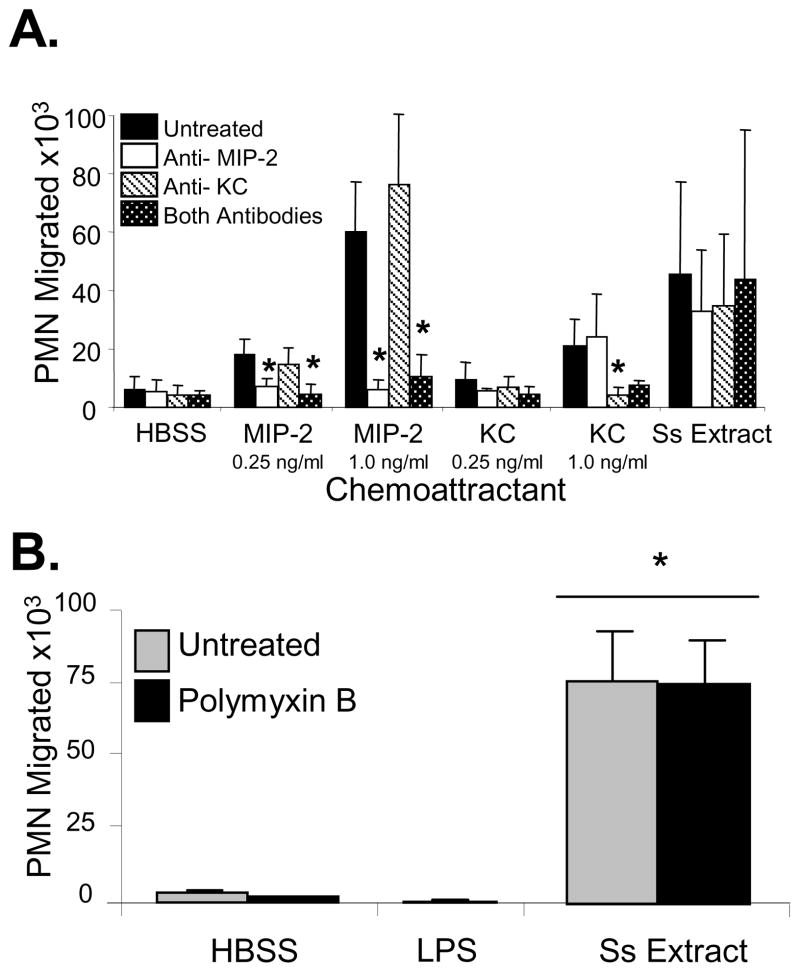
Figure 3. Neutrophils are recruited to S. stercoralis soluble extract in vitro and not to the chemokines MIP-2 and KC released by the neutrophils after culture with the S. stercoralis soluble extract and not to contaminating LPS.
(A) Chemotaxis assays were performed with MIP-2 and KC added to the bottom wells at the concentrations of 0.25 and 1.0 ng/ml. Antibodies against MIP-2 and KC were added to the wells to block the activity of the chemokines and to test if the antibodies would block the migration of the neutrophils (PMN) to the S. stercoralis soluble extract (Ss Extract). An asterisk indicates a statistically significant decrease (p<0.05) in the number of neutrophils recruited after treatment with antibody. (B) Neutrophil chemotaxis analyses were performed using transwell migration assays to 1, 10 or 100 ng/ml of LPS or S. stercoralis soluble extract (SsExtract) in HBSS with or without polymyxin B pretreatment to block LPS in the bottom well. All doses of LPS gave equivalent results and the response to100 ng/ml is reported. An asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference (p<0.05) compared to migration of cells to the control HBSS. The data presented is the mean ± standard error of five independent experiments.