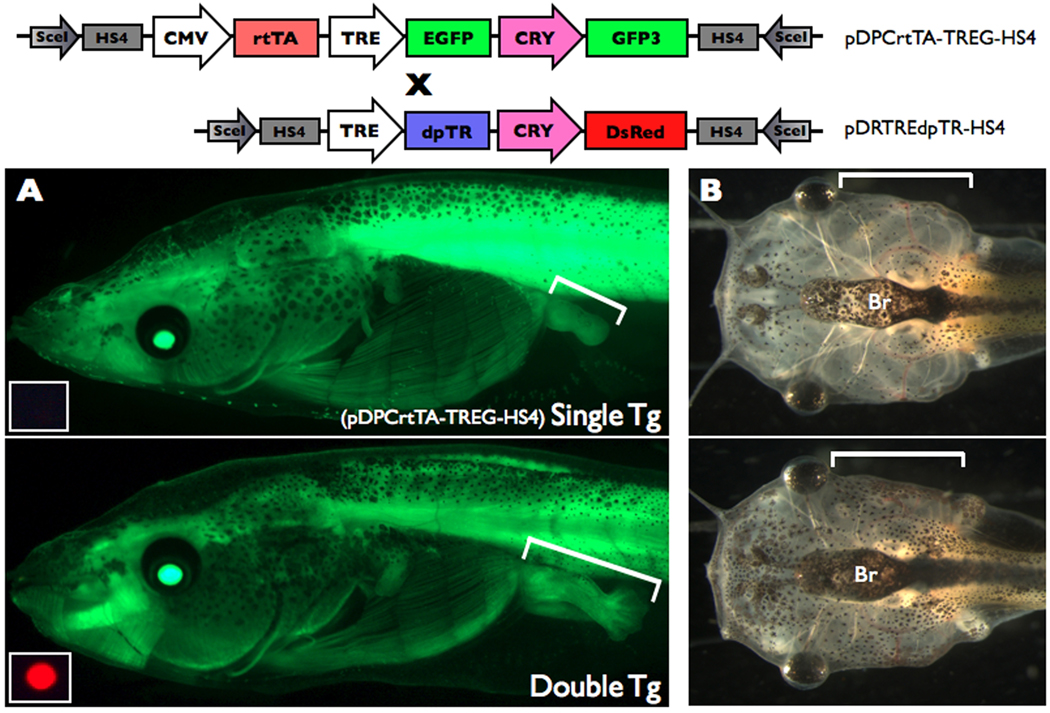
Figure 4.
Dox-induced dpTR causes metamorphic phenotypes. Double transgenic tadpoles for the two constructs shown were treated with 50 ug/mL Dox beginning at NF stage 49 for 12 days (4 tads/200mL with changing and feeding every 2nd day). Tadpoles singly transgenic for pDPCrtTA-TREG-HS4 was similarly treated and used as a control. A. GFP expression present all over the body in single (top) and double (bottom) transgenic animals from Dox-activated rtTA induced GFP from the TRE:GFP cassette in pDPCrtTA-TREG-HS4 was visualized using fluorescence microscopy. Hindlimbs are indicated by brackets. The small inset at the bottom left of each green fluorescence image is the red fluorescence image cropped around the eye to reveal the absence or presence of the pDRTREdpTR-HS4 transgene. The same camera settings were used in both panels. Representative individuals from n=13 single transgenics and n=7 double transgenics for Dox-treated tadpoles starting at NF49–52. B. The gills in the double transgenic animals (bottom) and the single transgenic tadpole (top) are indicated by brackets. The same camera settings were used in both panels. Representative individuals from n=3 single transgenics and n=2 double transgenics for Dox-treated tadpoles starting at NF49.