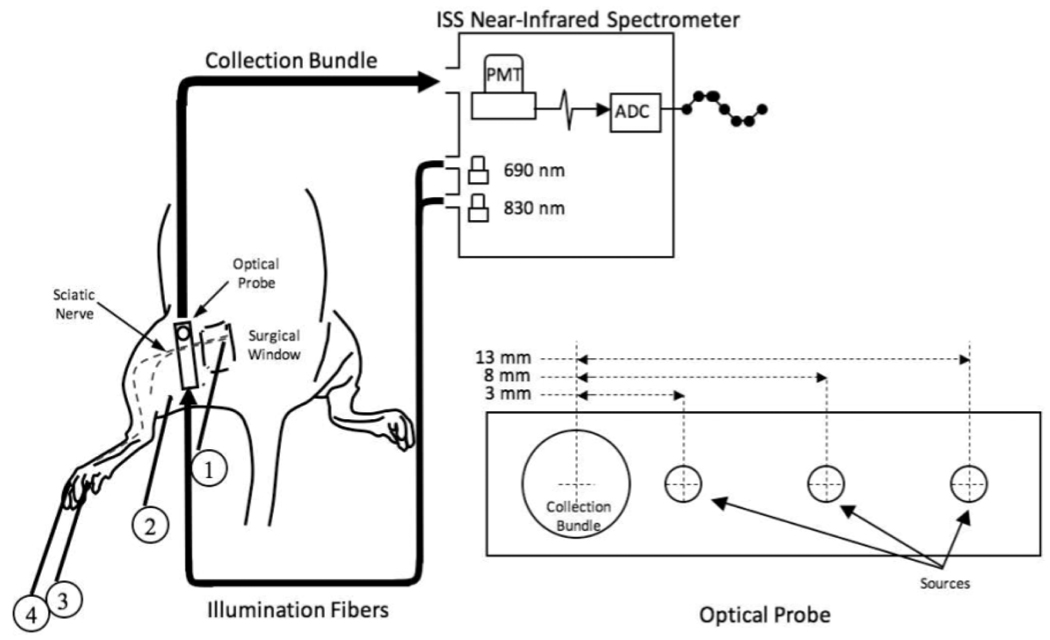
Figure 3.
Experimental setup for the animal model. A surgical window was created over the proximal course of the left sciatic nerve in Sprague-Dawley rats. A non-invasive optical probe delivering 690 and 830 nm light at 3 different source-detector separation distances was coupled to the PMT of a frequency-domain spectrometer and oriented perpendicularly to the course of the nerve. 60 × 600 ms epochs, each synchronized to the delivery of a 0.1 ms current stimulus to the exposed nerve (1), were averaged to generate an optical response. Simultaneously, electrophysiological responses to the stimulus were recorded from the plantar muscles of the left foot. (2) ground electrode, (3) active recording electrode, (4) reference electrode.