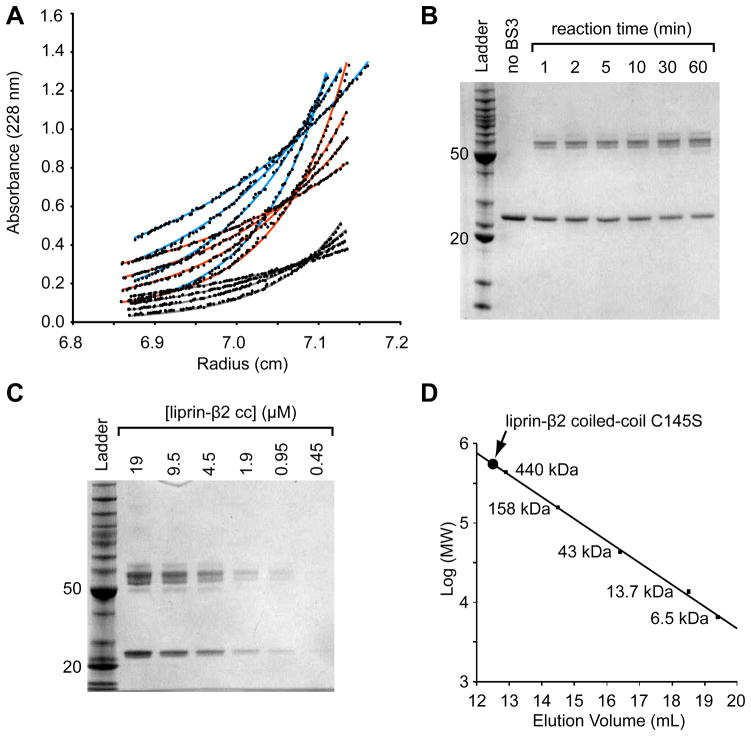
Figure 2. The Liprin-β2 Coiled-Coil Forms an Extended Dimer.
(A) The liprin-β2 coiled-coil domain concentration distributions after sedimentation to equilibrium at various speeds and protein concentrations. The three different concentrations (light blue - 0.18 mg/mL, orange - 0.12 mg/mL, and grey - 0.059 mg/mL) were equilibrated at four different speeds (10, 12, 14, and 17 krpm, bottom to top) and globally fit to a single exponential (shown as lines) with a variable molecular weight. The data was best fit with the molecular weight equal to the dimer (52,598 Da measured from fit; 53,984.8 calculated from sequence). (B) An SDS-PAGE gel showing the results of a liprin-β2 coiled-coil domain chemical cross-linking time-series experiment performed using a constant concentration of protein (5 μM) and BS3 cross-linker (50 μM). (C) An SDS-PAGE gel showing the results of a chemical cross-linking of the liprin-β2 coiled-coil domain at different protein concentrations, at a constant BS3 cross-linker concentration (100 μM) for a total time of 5 min. The ladder used for the gels in B and C contains standard proteins of 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 120, 160, and 220 kDa (BenchMark Protein Ladder, Invitrogen). For reference the 20 and 50 kDa bands of the ladder are indicated on each gel. (D) Superdex S-200 gel filtration chromatography of the liprin-β2 coiled-coil domain C145S. The elution volume of a set of globular protein standards is also indicated. The protein standards from largest to smallest are ferritin, aldolase, ovalbumin, ribonuclease A, and aprotinin (GE Healthcare). The void volume of the column was determined using blue dextran 2000 to be approximately 8.3 mL. The liprin-β2 coiled-coil (concentration < 0.5 mg/mL) elutes at 12.6 mL (~525 kDa) or approximately 20-fold higher than its monomeric molecular weight.