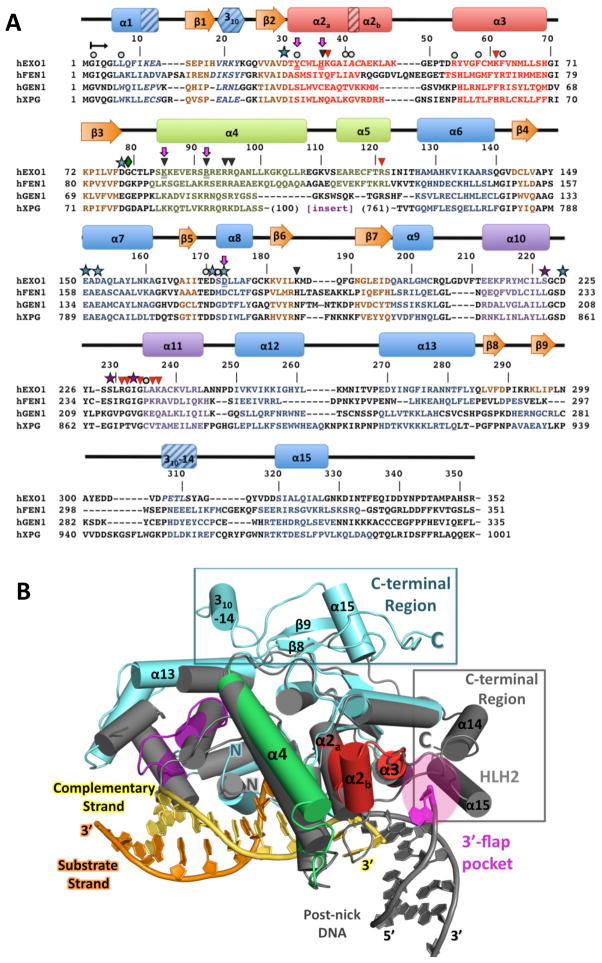
Figure 2. Structure and sequence alignments of hExo1 with other human 5′ structure-specific nuclease superfamily members.
(A) Structure-based sequence alignment of human 5′ structure-specific nuclease family members. Residues with assigned secondary structure are colored as in Figure 1. 310-helices are shown with diagonal lines. Note that the sequence of the large spacer region (insert) in hXPG is not shown. hExo1 residues mutated in this study are underlined and highlighted with purple arrows. Functionally important residues are indicated: conserved acidic residues in the active site, blue stars; K+-chelating residues, purple stars; interactions with complementary (non-substrate) DNA strand, black triangles; interactions with DNA substrate strand, red triangles; van der Waals contacts with DNA, grey circles. (B) Comparison of hExo1 with FEN-1. Alignment of structures of hExo1 (teal; motifs colored as in 2A) and A. fulgidus FEN-1 (grey; PDB ID 1RXW) Structures reveal significant divergence in the C-terminal region (boxed), and the 3′ flap binding motif of FEN-1 (magenta).