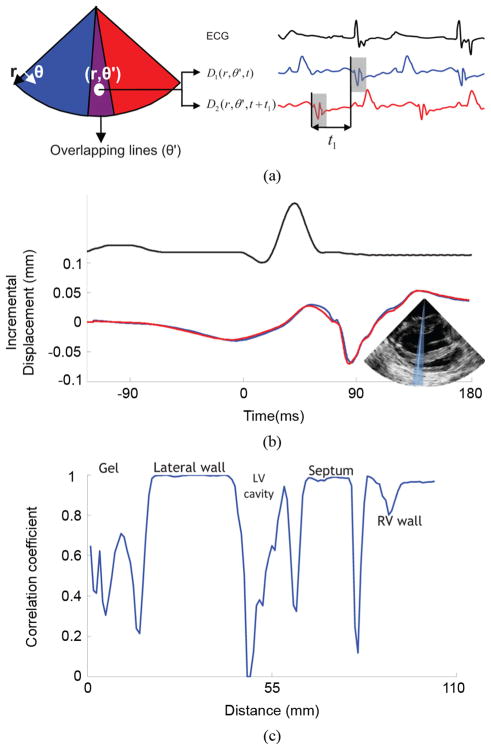
Fig. 2.
Illustration of the motion-matching method. (a) Axial incremental displacement is estimated twice in the overlapping RF-beams: once when sector 1 is acquired, and once when sector 2 is acquired. Assuming the periodicity of the heart, cross-correlation between those two independent acquisitions provides the time delay between the two sectors. (b) Incremental axial displacement over time of a sample located in the lateral wall acquired from an overlapping RF-beam. The blue line was acquired with sector 1 and the red line, with sector 2. One can observe the similarity between the two curves and the experimental periodicity of the heart’s incremental displacements. (c) Cross-correlation coefficients of the incremental axial displacement over time along an overlapping RF-beam. These coefficients are close to 1 in the myocardial tissue, and dramatically drop in the cavity and in the ultrasound gel.