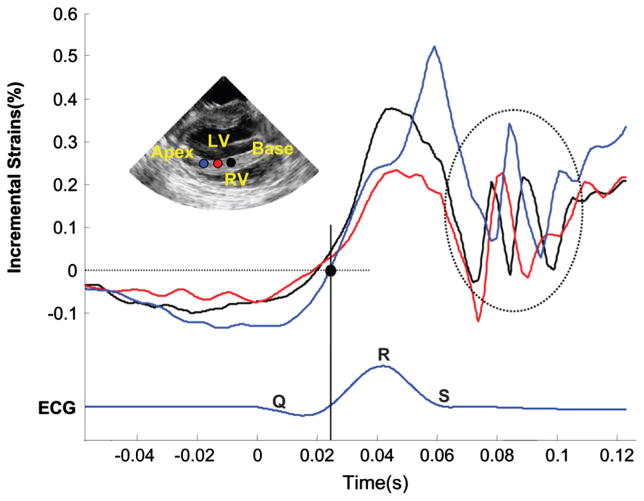
Fig. 3.
Temporal variation of the incremental strains along three points in the septum in the vicinity of the QRS complex. The electromechanical wave (EMW) is defined by the point at which the incremental strains change sign. The EMW is initiated at the endocardial surface of the septum (red) and travels towards the base (black) and the apex (blue). Oscillations (dashed circle) are also observed following the mitral valve closure. These travel from base (black) to apex (blue).