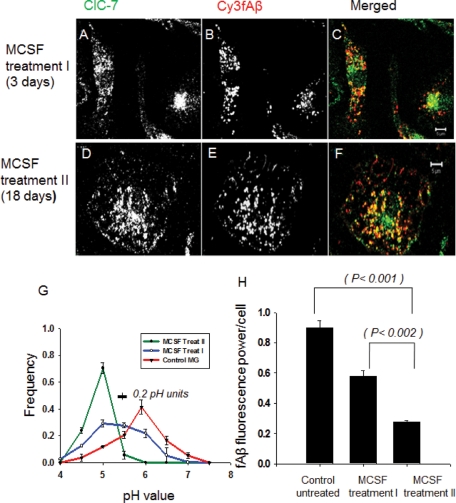
FIGURE 2:
Activation of primary mouse microglia with MCSF recruits ClC-7 to lysosomes and leads to lysosomal acidification and fAβ degradation. (A–C) Immunolocalization of ClC-7 (green) as compared with Cy3fAβ (red) that had been endocytosed and delivered to lysosomes in cells subject to MCSF Treatment I. (D–F) Immunolocalization of ClC-7 (green) as compared with Cy3fAβ (red) that had been endocytosed and delivered to lysosomes in cells subject to MCSF Treatment II. The images are single slices from a confocal stack. Bar: 5 μm. (G) Frequency distribution of lysosomal pH in microglia receiving MCSF Treatment II (green curve), MCSF Treatment I (blue curve), or control microglia (red curve). The values plotted are the fraction of lysosomes with pH values in the interval within ±0.25 pH units of the indicated value (e.g., 4.75–5.25 for pH 5.0). Error bars represent SEM. The horizontal bar on the figure shows the SD for the measurement of pH values of single lysosomes in cells fixed at pH 5.5. We analyzed the distribution of fluorescein/rhodamine fluorescence ratio values in (fluorescein-rhodamine)-dextran-loaded lysosomes to test for significance in the differences in the pH distributions. The distributions for both MCSF-treated cells differed from the distribution in control cells (p < 0.0001 for MCSF II and p < 0.001 for MCSF I treatments). (H) Degradation of Cy3fAβ by microglial cells receiving MCSF Treatment I or II. Cy3 fluorescence retained inside the cells 72 h after a 1-h uptake of Cy3fAβ is shown. Error bars represent SEM, and p values are obtained using Student's t test (two tailed).