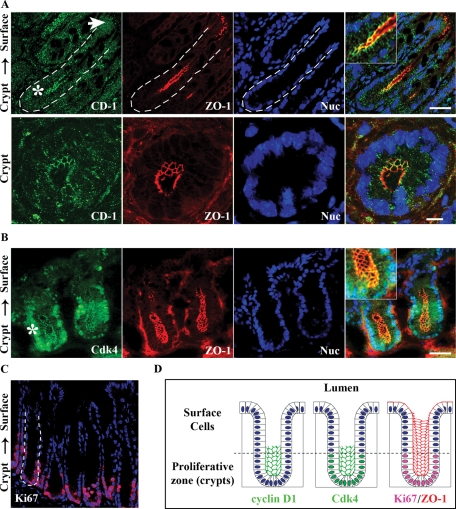
FIGURE 1:
Cyclin D1 and Cdk4 localize at TJs in intestinal epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro. (A) Immunofluorescence imaging of cyclin D1 (green) colocalization with ZO-1 (red) in crypt epithelia of murine distal colon tissue. Nuclei are stained with Topro-3 (blue). White arrow designates epithelial surface cells facing the lumen; the asterisk designates crypt regions. Scale bar = 40 μm. Merged inset at 2× magnification. Bottom panels: Magnified view of murine colonic crypts. Scale bar = 10 μm. (B) Cdk4 (green) colocalizes with ZO-1 (red) in the base of colonic crypts. (C) Mouse distal colon crypts stained for the proliferation marker Ki67 (red) and nuclei (blue). (D) Schematic summarizing the immunofluorescence data with cyclin D1 and Cdk4 colocalizing with ZO-1 in colonic crypt epithelial cells. Cyclin D1 and Cdk4 are not present in lumen-facing surface cell populations, but appear restricted to the proliferative zone as marked by Ki67.