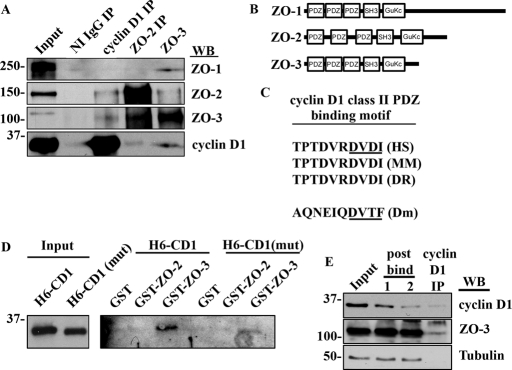
FIGURE 3:
Cyclin D1 forms a PDZ-dependent complex with ZO-3. (A) Western blot of IP experiments with nonimmune (NI) immunoglobulin (Ig)G, cyclin D1, ZO-2, and ZO-3. (B) Immunodepletion assay showing that only a fraction of ZO-3 is bound to cyclin D1 (C) Schematic diagram of ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3 showing multiple PDZ domains within ZO family proteins. (D) Amino acid sequence alignment of human (HS), murine (MM), zebrafish (DR), and Drosophila (Dm) cyclin D1 C-terminal tails showing a conserved class II PDZ binding motif (underlined). (E) GST–ZO-3 fusion proteins interact preferentially with His6–cyclin D1 (H6 CD-1) containing an intact PDZ binding motif and show attenuated binding to His6–cyclin D1 mutant lacking the putative C-terminal PDZ binding motif [H6-CD1(mut)]. (E) Immunodepletion assay showing retention of the majority of cellular ZO-3 in the postbind fractions after iterative cyclin D1 IP.