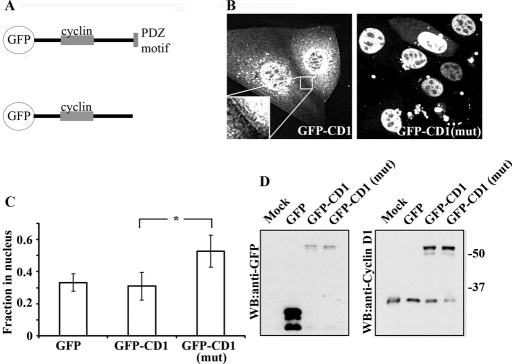
FIGURE 4:
The cyclin D1 PDZ motif is required for TJ localization. (A) Schematic representing GFP–cyclin D1 [GFP-CD-1 and GFP-CD-1(mut)] fusion constructs. (B) Live-cell imaging of GFP–cyclin D1, but not GFP–cyclin D1(mut), located to sights of cell–cell contact (see inset). GFP–cyclin D1(mut) is predominantly localized within the nucleus (right panel). (C) Subcellular localization analysis of overexpressed GFP, GFP–cyclin D1, or GFP–cyclin D1(mut) in paraformaldehyde-fixed SKCO-15 cells. Ablation of cyclin D1 C-terminal PDZ binding motif results in redistribution of cyclin D1 to the nucleus (*p < 0.001, n = 40 cells per condition per experiment; n = 3). (D) Western blot of mock transfected, GFP-, GFP–cyclin D1–, or GFP–cyclin D1(mut)–expressing SKCO-15 cells with anti-GFP (left panel) and anti-cyclin D1 (right panel).