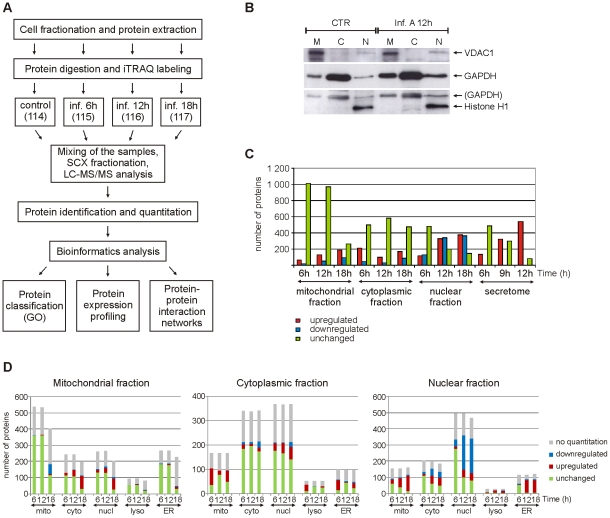
Figure 1. Quantitative subcellular proteome and secretome analysis of influenza A virus-infected human primary macrophages.
A. Workflow of the experiment. GO = gene ontology. B. Western blot analysis of control and influenza A virus-infected cells from mitochondrial (M), cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions using mitochondrial, cytoplasmic and nuclear markers (voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 (VDAC1), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and histone H1, respectively). C. Numbers of reliably quantified and differentially regulated proteins (fold difference ≥1,5 or ≤0,67 for intracellular fractions and ≥3 for secretome) in each subcellular fraction and secretome at different timepoints. D. Gene ontology-based classification of all the proteins identified from intracellular fractions. Mitochondrial, cytoplasmic, nuclear, lysosomal and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) annotations for the identified proteins are shown.